Mastering Java Development Kit: Essential Tools for Java Programmers
The Java Development Kit (JDK): Everything You Need to Know
Java is a popular programming language used for developing a wide range of applications, from simple desktop tools to complex enterprise systems. At the core of Java development is the Java Development Kit (JDK), a crucial set of tools that every Java developer needs to have.
What is the JDK?
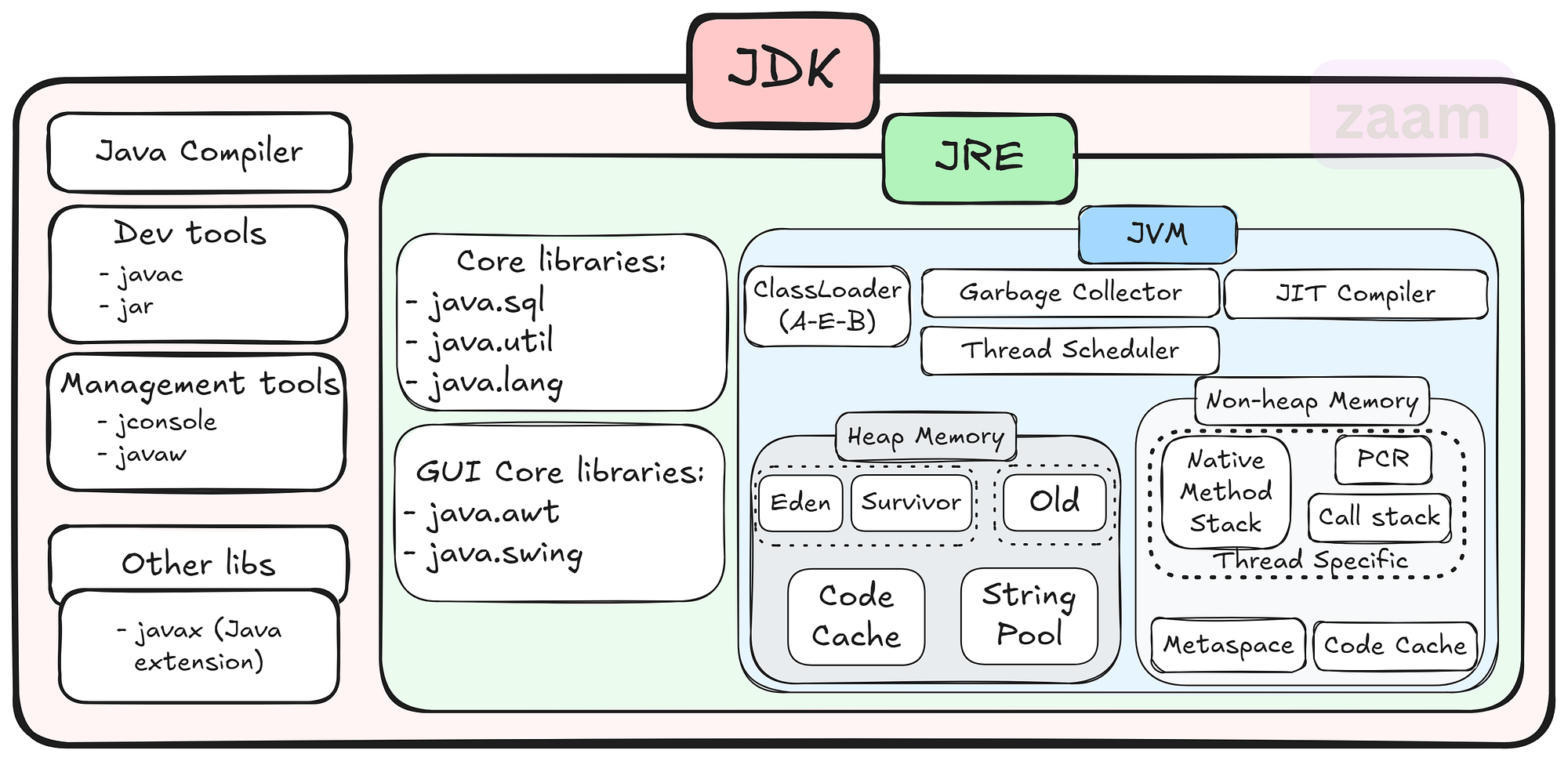
The JDK is a software development kit that provides all the necessary tools and libraries for developing Java applications. It includes the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), which is required for running Java programs, as well as development tools such as the Java compiler, debugger, and other utilities.
Key Components of the JDK
Some of the key components of the JDK include:
- Java Compiler: The javac compiler converts Java source code into bytecode that can be executed by the JVM.
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM): The JVM is responsible for executing Java bytecode on different platforms.
- Java Class Library: A collection of pre-written classes and interfaces that provide core functionality for Java applications.
- Development Tools: Tools like Javadoc for generating API documentation, JAR for packaging applications, and more.
Why Use the JDK?
The JDK is essential for Java developers because it provides everything needed to write, compile, debug, and run Java applications. By using the JDK, developers can ensure that their code is compatible with different platforms and environments thanks to the JVM’s portability.
Getting Started with the JDK
To start using the JDK, developers can download it from Oracle’s website or other authorized sources. Installation instructions are typically provided with the download package, making it easy to set up and start developing in Java.
Conclusion
The JDK plays a vital role in Java development by providing developers with all the necessary tools and libraries to create powerful and scalable applications. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, having a solid understanding of the JDK is essential for success in Java programming.
8 Key Advantages of the Java Development Kit for Developers
- Comprehensive set of tools for Java development
- Includes the Java compiler for converting source code to bytecode
- Provides a rich collection of libraries for building robust applications
- Cross-platform compatibility with the Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- Supports object-oriented programming principles
- Integrated development environment (IDE) support for coding convenience
- Regular updates and improvements from Oracle and the Java community
- Extensive documentation and resources available online for learning and troubleshooting
Challenges of the Java Development Kit: Size, Complexity, Resource Demands, and Compatibility Issues
Comprehensive set of tools for Java development
The Java Development Kit (JDK) stands out for its comprehensive set of tools tailored for Java development. From the Java compiler to debugging utilities and class libraries, the JDK equips developers with everything they need to efficiently write, compile, and debug Java applications. This extensive toolkit not only streamlines the development process but also ensures that developers have access to a wide array of resources to tackle various aspects of Java programming effectively.
Includes the Java compiler for converting source code to bytecode
The Java Development Kit (JDK) offers a significant advantage by including the Java compiler, a crucial tool for converting source code into bytecode. This feature simplifies the development process for Java programmers, allowing them to write code in a human-readable format and then compile it into bytecode that can be executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). By bundling the compiler with the JDK, developers can seamlessly transition from writing code to testing and running their applications without the need for additional tools or configurations.
Provides a rich collection of libraries for building robust applications
The Java Development Kit (JDK) stands out for its ability to provide a rich collection of libraries that empower developers to build robust applications with ease. These libraries offer a wide range of pre-written classes and interfaces that cover various functionalities, saving developers time and effort in coding from scratch. By leveraging the extensive library support within the JDK, developers can enhance the functionality and performance of their applications while ensuring scalability and reliability in their software projects.
Cross-platform compatibility with the Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
The Java Development Kit (JDK) offers a significant advantage with its cross-platform compatibility through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). This feature allows Java applications to run on various operating systems without the need for recompilation, ensuring seamless deployment across different platforms. By leveraging the JVM, developers can write code once and have it executed on Windows, macOS, Linux, and other supported environments, making Java a versatile choice for creating applications that reach a wide audience.
Supports object-oriented programming principles
Java Development Kit (JDK) offers a significant advantage by supporting object-oriented programming principles. Object-oriented programming allows developers to organize code into reusable and modular components, enhancing code readability, maintainability, and scalability. With the JDK’s support for object-oriented programming, developers can easily create complex applications by leveraging concepts such as classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism, leading to more efficient and robust software development processes.
Integrated development environment (IDE) support for coding convenience
The Java Development Kit (JDK) offers integrated development environment (IDE) support, providing developers with a user-friendly platform for coding convenience. With IDE tools tailored for Java development, programmers can benefit from features like code completion, syntax highlighting, debugging capabilities, and project management tools. This support streamlines the coding process, enhances productivity, and helps developers write high-quality Java applications efficiently.
Regular updates and improvements from Oracle and the Java community
Regular updates and improvements from Oracle and the Java community ensure that the Java Development Kit (JDK) remains a cutting-edge tool for developers. By staying current with the latest advancements, developers can benefit from enhanced performance, security patches, and new features that help streamline their development process and keep their applications up-to-date with industry standards. This commitment to continuous improvement demonstrates the dedication of both Oracle and the Java community to support developers in creating robust and innovative Java applications.
Extensive documentation and resources available online for learning and troubleshooting
Java Development Kit (JDK) offers a significant advantage with its extensive documentation and abundant online resources available for learning and troubleshooting. Whether you are a novice Java developer looking to grasp the basics or an experienced programmer seeking solutions to complex issues, the wealth of online materials ensures that you have the support and guidance needed to enhance your Java development skills effectively. The comprehensive documentation and resources associated with JDK empower developers to overcome challenges, explore new features, and continuously improve their proficiency in Java programming.
Large Size
The Java Development Kit (JDK) has a notable downside in its large size, which can demand a considerable amount of storage space on your system. Due to its extensive collection of tools, libraries, and resources, the JDK’s size may pose a challenge for users with limited storage capacity, potentially impacting the availability of space for other applications or files on the system. This aspect of the JDK’s size underscores the importance of considering storage requirements when installing and using this development kit for Java programming projects.
Complexity
Java development using the JDK can present a significant challenge in terms of complexity, particularly for beginners. The extensive toolset provided by the JDK can be overwhelming for those new to Java programming, making it difficult to grasp all the functionalities and how they interact. Navigating through the various tools and libraries within the JDK may require a steep learning curve, potentially slowing down the development process and causing frustration for inexperienced developers.
Resource Intensive
One significant drawback of using the Java Development Kit (JDK) is its resource-intensive nature. Running Java applications developed with the JDK may demand higher system resources compared to applications built with other programming languages. This increased resource requirement can lead to higher memory consumption and slower performance on devices with limited capabilities, potentially affecting the overall efficiency and responsiveness of the application.
Updates and Compatibility
Keeping up with JDK updates and ensuring compatibility with different versions can be challenging for Java developers. As new updates are released regularly to enhance performance, security, and features, developers need to stay vigilant in updating their development environments and ensuring that their code remains compatible with the latest JDK versions. This process can be time-consuming and may require adjustments to existing codebases to avoid potential compatibility issues. Additionally, managing dependencies and third-party libraries to align with JDK updates adds another layer of complexity to the development process.