Exploring the Exciting Features of Java’s Latest Version
Exploring the Latest Version of Java
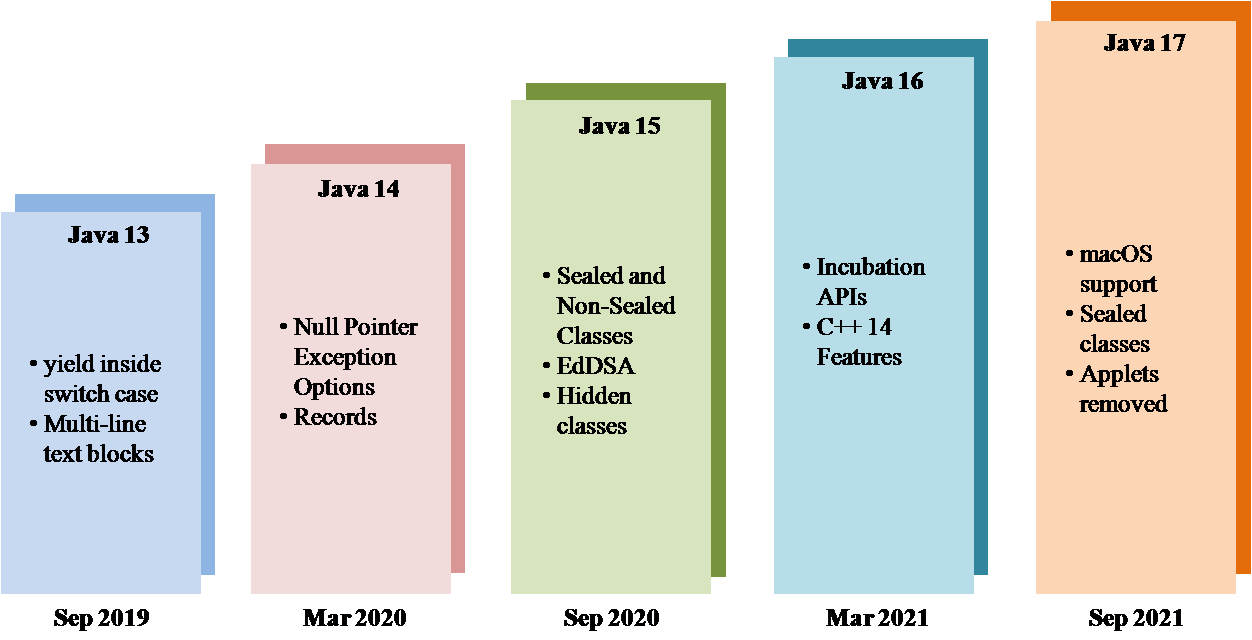
Java, one of the most popular programming languages in the world, continues to evolve with each new version. The latest release, Java 17, brings a host of new features and improvements that enhance developer productivity and application performance.
New Features in Java 17:
- JEP 356: Enhanced Pseudo-Random Number Generators – Java 17 introduces new interfaces and implementations for pseudo-random number generators, offering developers more flexibility and control over random number generation in their applications.
- JEP 382: New macOS Rendering Pipeline – With Java 17, macOS users can benefit from a new rendering pipeline that improves the performance and user experience of Java applications on Apple’s operating system.
- JEP 391: macOS/AArch64 Port – This enhancement brings official support for running Java applications on macOS devices powered by Apple Silicon chips, further expanding Java’s compatibility across different hardware architectures.
- JEP 411: Deprecate Security Manager for Removal – In an effort to simplify and modernize the platform, Java 17 deprecates the Security Manager feature with plans to remove it in a future release. Developers are encouraged to migrate away from using Security Manager in their applications.
Performance Improvements:
In addition to new features, Java 17 also includes various performance enhancements aimed at optimizing the execution speed and memory efficiency of Java applications. Developers can expect improved runtime performance and reduced memory footprint when using the latest version of Java.
Upgrade Considerations:
For developers considering upgrading to Java 17, it is important to review the release notes and ensure compatibility with existing codebases and third-party libraries. Testing your applications on the new version is recommended to identify any potential issues or compatibility concerns before deploying them into production environments.
Overall, Java 17 represents another significant milestone in the ongoing evolution of the language, offering developers new tools and capabilities to build robust and efficient software solutions. Whether you are a seasoned Java developer or just starting with the language, exploring the latest version of Java can open up exciting possibilities for your projects.
Everything You Need to Know About the Latest Version of Java: FAQs and Key Insights
- What is the latest version of Java?
- What are the new features in the latest version of Java?
- How can I upgrade to the latest version of Java?
- Is it necessary to update to the latest version of Java?
- Are there any performance improvements in the latest version of Java?
- What considerations should I take into account before upgrading to the latest version of Java?
- Is Java 17 backward compatible with previous versions?
- Where can I find more information about the changes and updates in the latest version of Java?
What is the latest version of Java?
The latest version of Java is Java 17. Released with a range of new features and performance improvements, Java 17 continues to enhance developer productivity and application efficiency. With updates such as enhanced pseudo-random number generators, a new macOS rendering pipeline, and official support for macOS devices powered by Apple Silicon chips, Java 17 offers developers more flexibility and compatibility across different platforms. It is recommended for developers to stay up-to-date with the latest version of Java to leverage its advancements and ensure optimal performance in their projects.
What are the new features in the latest version of Java?
The latest version of Java, Java 17, introduces a range of new features that enhance developer productivity and application performance. Some of the key enhancements include an enhanced pseudo-random number generator system (JEP 356) that provides developers with more flexibility in random number generation. Additionally, macOS users benefit from a new rendering pipeline (JEP 382) that improves the performance of Java applications on Apple’s operating system. Furthermore, the introduction of official support for running Java applications on macOS devices powered by Apple Silicon chips (JEP 391) expands Java’s compatibility across different hardware architectures. Lastly, Java 17 deprecates the Security Manager feature for future removal (JEP 411), encouraging developers to migrate away from using it in their applications. These new features in Java 17 demonstrate the language’s commitment to innovation and improvement in each release.
How can I upgrade to the latest version of Java?
To upgrade to the latest version of Java, you can follow a few simple steps. First, visit the official Java website to download the newest version of Java. Make sure to select the appropriate version for your operating system. Next, run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process. If you already have an older version of Java installed on your system, the installer may prompt you to uninstall it before proceeding with the upgrade. Once the installation is complete, restart your computer to apply the changes. By keeping your Java installation up-to-date, you can benefit from enhanced features, improved performance, and important security updates provided in the latest version.
Is it necessary to update to the latest version of Java?
It is often recommended to update to the latest version of Java to ensure that your applications benefit from the newest features, performance improvements, and security enhancements offered by the updated release. Staying up-to-date with Java versions can help address vulnerabilities, improve compatibility with modern systems, and optimize the overall performance of your software. However, the decision to update should also consider factors such as compatibility with existing codebases and third-party libraries, as well as any potential impact on production environments. Regularly evaluating the benefits and implications of upgrading to the latest version of Java can help developers make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and requirements.
Are there any performance improvements in the latest version of Java?
In the latest version of Java, developers can expect to see notable performance improvements that enhance the overall execution speed and memory efficiency of Java applications. These enhancements are designed to optimize runtime performance and reduce the memory footprint, resulting in better responsiveness and scalability for Java-based software. By leveraging the performance improvements in the latest Java version, developers can create more efficient and high-performing applications that meet the demands of modern computing environments.
What considerations should I take into account before upgrading to the latest version of Java?
Before upgrading to the latest version of Java, there are several considerations that developers should keep in mind. Firstly, it is crucial to review the release notes of the new version to understand the changes, new features, and potential compatibility issues that may arise with existing codebases or third-party libraries. Testing your applications on the new version is highly recommended to identify any bugs or issues before deploying them into production environments. Additionally, ensuring that all dependencies and tools used in your projects are compatible with the latest Java version is essential to prevent any disruptions in your development workflow. By carefully evaluating these factors and preparing accordingly, developers can smoothly transition to the latest version of Java and take advantage of its enhanced features and performance improvements.
Is Java 17 backward compatible with previous versions?
Java 17 maintains Java’s strong commitment to backward compatibility with previous versions. Developers can rest assured that applications written in earlier versions of Java will continue to run seamlessly on Java 17 without requiring any modifications. This backward compatibility ensures that existing codebases and libraries can be easily migrated to the latest version, allowing developers to leverage the new features and improvements in Java 17 while maintaining the stability and reliability of their applications.
Where can I find more information about the changes and updates in the latest version of Java?
If you are looking for more information about the changes and updates in the latest version of Java, a good place to start is the official Java website. The Java website typically provides detailed release notes and documentation that highlight the new features, enhancements, and performance improvements introduced in the latest version of the language. Additionally, developer forums, tech blogs, and online communities dedicated to Java programming often discuss and analyze the changes in the latest Java release, offering insights and practical examples to help developers understand and leverage the new features effectively. By exploring these resources, you can stay informed about the latest developments in Java and make informed decisions when upgrading your projects to the newest version.