Revolutionizing Development with RAD Software
The Power of RAD Software Development
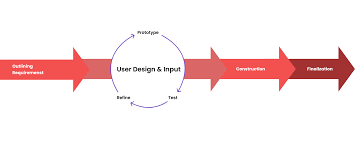
Rapid Application Development (RAD) software is revolutionizing the way applications are built and deployed. With its agile approach and focus on user feedback, RAD software development has become a popular choice for businesses looking to streamline their development processes and deliver high-quality applications quickly.
One of the key advantages of RAD software is its ability to accelerate the development cycle. By emphasizing iterative development and prototyping, RAD enables developers to quickly build and test functional prototypes, gather feedback from users, and make necessary adjustments in a timely manner.
Furthermore, RAD software promotes collaboration between developers and stakeholders. With its user-centric approach, RAD encourages regular communication with end-users to ensure that the final product meets their needs and expectations. This collaborative process helps reduce the risk of misunderstandings and ensures that the application aligns with the intended use cases.
Another benefit of RAD software is its flexibility in accommodating changes throughout the development process. Unlike traditional waterfall methods that follow a rigid sequence of stages, RAD allows for modifications to be made at any point, enabling teams to adapt to evolving requirements and market conditions swiftly.
Overall, RAD software empowers businesses to deliver innovative solutions faster, improve customer satisfaction, and stay ahead of the competition in today’s dynamic digital landscape. By embracing RAD principles and leveraging advanced tools, organizations can unlock new opportunities for growth and success in the ever-evolving world of software development.
6 Key Advantages of RAD Software: Boosting Development Speed, Collaboration, and Innovation
- Accelerates development cycle
- Promotes collaboration between developers and stakeholders
- Allows for flexibility in accommodating changes
- Facilitates rapid prototyping and user feedback
- Enhances innovation and creativity in application development
- Helps businesses stay competitive in the dynamic digital landscape
Challenges of RAD Software: Managing Flexibility, Stakeholder Engagement, and Compliance
- Potential for scope creep due to flexibility in accommodating changes
- Requires active involvement and collaboration from stakeholders throughout the development process
- May not be suitable for projects with strict regulatory or compliance requirements
Accelerates development cycle
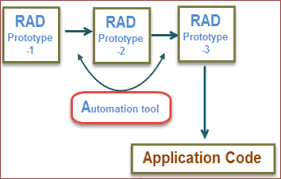
One of the significant advantages of RAD software is its ability to accelerate the development cycle. By focusing on iterative development and prototyping, RAD enables teams to quickly build functional prototypes, gather user feedback, and make necessary adjustments promptly. This streamlined approach not only speeds up the development process but also allows for rapid testing and refinement of features, ultimately leading to faster delivery of high-quality applications to meet market demands efficiently.
Promotes collaboration between developers and stakeholders
One significant advantage of RAD software is its ability to foster collaboration between developers and stakeholders. By encouraging regular communication and feedback exchange, RAD ensures that all parties are actively involved in the development process. This collaborative approach helps align the project with the stakeholders’ requirements and expectations, leading to a more user-centric and successful end product. The continuous engagement between developers and stakeholders in RAD software development enhances transparency, promotes shared understanding, and ultimately results in delivering solutions that meet the desired outcomes effectively.
Allows for flexibility in accommodating changes
One of the significant advantages of RAD software is its flexibility in accommodating changes throughout the development process. Unlike traditional methods that follow a rigid sequence of stages, RAD allows for modifications to be made at any point. This adaptability enables teams to respond quickly to evolving requirements, feedback, or market conditions, ensuring that the final product meets the most current needs and expectations. The ability to incorporate changes seamlessly enhances the agility and responsiveness of development teams, ultimately leading to more innovative and customer-centric solutions.
Facilitates rapid prototyping and user feedback
Rapid Application Development (RAD) software excels in facilitating rapid prototyping and user feedback, enabling developers to quickly create functional prototypes and gather valuable insights from end-users. By streamlining the prototyping process and encouraging continuous user engagement, RAD software empowers teams to iterate efficiently, address user needs promptly, and deliver solutions that align closely with user expectations. This approach not only accelerates the development cycle but also ensures that the final product meets the desired usability and functionality criteria, ultimately leading to enhanced user satisfaction and product success.
Enhances innovation and creativity in application development
Rapid Application Development (RAD) software excels in enhancing innovation and creativity in application development by fostering a dynamic and iterative approach to the design process. With its emphasis on quick prototyping and user feedback, RAD encourages developers to experiment with new ideas, features, and functionalities, pushing the boundaries of traditional development methods. This creative freedom not only leads to the discovery of novel solutions but also enables teams to adapt quickly to changing market demands and user preferences, ultimately driving continuous innovation in application development.
Helps businesses stay competitive in the dynamic digital landscape
Rapid Application Development (RAD) software plays a crucial role in helping businesses stay competitive in the dynamic digital landscape. By enabling faster development cycles and iterative prototyping, RAD software allows companies to adapt quickly to changing market demands and technological advancements. This agility not only helps businesses deliver innovative solutions promptly but also ensures they can respond effectively to competitors’ moves and evolving customer preferences. In a fast-paced digital environment where speed and flexibility are key, embracing RAD software gives businesses a significant edge in staying relevant and competitive in their industry.
Potential for scope creep due to flexibility in accommodating changes
One significant drawback of RAD software development is the potential for scope creep resulting from its flexibility in accommodating changes. While the ability to make adjustments throughout the development process can be beneficial, it also opens the door to continuous modifications that may expand the project beyond its original scope. This can lead to increased project timelines, budget overruns, and a lack of clear direction, ultimately impacting the overall success of the project. It is essential for teams utilizing RAD methodologies to establish robust change management processes and maintain a clear understanding of project requirements to mitigate the risks associated with scope creep.
Requires active involvement and collaboration from stakeholders throughout the development process
One potential drawback of RAD software is its requirement for active involvement and collaboration from stakeholders throughout the development process. While this emphasis on continuous engagement can lead to better alignment with user needs and expectations, it also demands a significant time commitment from stakeholders. This level of involvement may not always be feasible for all parties involved, leading to potential delays or difficulties in decision-making. Additionally, conflicting viewpoints or changing requirements from stakeholders can introduce complexities that may impact the overall efficiency and progress of the RAD development cycle.
May not be suitable for projects with strict regulatory or compliance requirements
Rapid Application Development (RAD) software may not be suitable for projects with strict regulatory or compliance requirements. Due to its iterative and flexible nature, RAD may struggle to adhere to stringent guidelines and regulations that govern certain industries. Projects that demand meticulous documentation, rigorous testing protocols, and extensive validation processes may find RAD methodology challenging to meet the necessary compliance standards. In such cases, a more structured and methodical approach to software development may be required to ensure full adherence to regulatory frameworks and industry standards.