Exploring the Traditional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Approach
The Traditional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Software development is a complex process that involves various stages to ensure the successful creation of a software product. One of the most common approaches to software development is the Traditional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
Stages of the Traditional SDLC:
- Planning: This initial stage involves defining the scope of the project, setting goals, and establishing a timeline for development.
- Analysis: In this stage, requirements are gathered from stakeholders and analyzed to determine the functionality needed in the software.
- Design: The design phase involves creating a detailed blueprint of how the software will look and function based on the requirements gathered in the analysis stage.
- Implementation: During implementation, developers write code based on the design specifications and integrate different components to create the software.
- Testing: Testing is a crucial phase where developers test the software for bugs, errors, and performance issues to ensure it meets quality standards.
- Maintenance: Once the software is deployed, maintenance involves making updates, fixing bugs, and addressing user feedback to keep the software running smoothly.
Advantages of Traditional SDLC:
- Predictability: The structured approach of traditional SDLC allows for better predictability in terms of project timelines and deliverables.
- Risk Management: By following a defined process with clear stages, risks can be identified early and mitigated effectively.
- Documentation: Each stage in traditional SDLC requires documentation, which helps in maintaining clarity and consistency throughout the development process.
The Traditional Software Development Life Cycle provides a systematic approach to software development that has been used successfully for many years. While newer methodologies like Agile have gained popularity for their flexibility and adaptability, traditional SDLC remains a valuable framework for projects that require strict adherence to requirements and processes.
Understanding Traditional SDLC: Key Phases and Differences from Modern Approaches
- What are the 7 steps in traditional SDLC?
- What is traditional system development?
- What are the traditional phases of software development?
- What are the five phases of the traditional SDLC?
- What is the difference between traditional SDLC and modern SDLC?
- What is the difference between traditional SDLC and Agile SDLC?
- What is a traditional SDLC?
What are the 7 steps in traditional SDLC?
In the Traditional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), there are typically seven key steps that outline the process of developing software. These steps include Planning, Analysis, Design, Implementation, Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance. Each step plays a crucial role in ensuring the successful creation and management of software products. From defining project goals and requirements to testing for quality assurance and maintaining the software post-deployment, these seven steps provide a structured framework for developers to follow throughout the development lifecycle.
What is traditional system development?
Traditional system development, also known as the Traditional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), refers to a structured approach to developing software applications. In traditional system development, the process follows a sequential order of stages, including planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. This methodology emphasizes thorough documentation, clear requirements gathering, and a step-by-step progression through each phase of development. While newer agile methodologies have gained popularity for their flexibility and iterative nature, traditional system development remains a reliable framework for projects that require a well-defined scope and adherence to predetermined processes.
What are the traditional phases of software development?
In traditional software development, the process typically consists of several well-defined phases that form the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). These phases include planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. During the planning phase, project goals and scope are defined. The analysis phase involves gathering and analyzing requirements from stakeholders. Design focuses on creating a detailed blueprint of the software’s structure and functionality. Implementation is where developers write code based on the design specifications. Testing ensures that the software meets quality standards before deployment. Maintenance involves ongoing updates and support to keep the software running smoothly. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring a systematic and structured approach to software development.
What are the five phases of the traditional SDLC?
In the Traditional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), there are five key phases that define the process of creating a software product. These phases include Planning, Analysis, Design, Implementation, and Testing. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring the successful development and deployment of software by systematically progressing from defining project requirements to testing the final product for quality and functionality. By following these structured phases, organizations can effectively manage software projects and deliver high-quality solutions that meet stakeholder expectations.
What is the difference between traditional SDLC and modern SDLC?
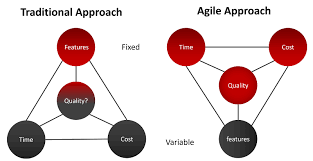
The main difference between traditional SDLC and modern SDLC lies in their approach to software development. Traditional SDLC, characterized by its sequential and linear process, follows a structured path from planning to maintenance with distinct stages like requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. On the other hand, modern SDLC methodologies such as Agile and DevOps emphasize flexibility, collaboration, and iterative development. Modern SDLC approaches allow for quicker adaptation to changing requirements, more frequent feedback loops with stakeholders, and a focus on delivering working software incrementally. While traditional SDLC provides predictability and thorough documentation throughout the development process, modern SDLC prioritizes responsiveness to change and customer needs.
What is the difference between traditional SDLC and Agile SDLC?
When comparing traditional SDLC with Agile SDLC, the key difference lies in their approach to software development. Traditional SDLC follows a sequential, linear process with distinct stages such as planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. In contrast, Agile SDLC is iterative and flexible, allowing for incremental development and frequent collaboration between cross-functional teams. While traditional SDLC emphasizes thorough planning and documentation upfront, Agile SDLC focuses on adaptability to changing requirements and continuous improvement through short development cycles known as sprints. Each approach has its strengths and is chosen based on the project’s specific needs for predictability and flexibility in software development.
What is a traditional SDLC?
A traditional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) refers to a structured approach to software development that follows a predefined set of stages from planning and analysis to design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. This methodical process aims to ensure that software projects are completed efficiently and effectively by breaking down the development process into distinct phases. Traditional SDLC emphasizes thorough documentation, clear requirements gathering, and sequential progression through each stage to deliver a high-quality software product that meets the specified criteria. While newer agile methodologies have gained popularity for their flexibility, traditional SDLC remains a reliable framework for projects requiring a more formal and predictable development approach.