Enhancing Software Security: A Guide to OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL)
Understanding OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL)
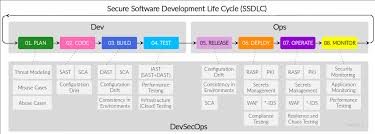
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a non-profit organization dedicated to improving the security of software. One of the key initiatives by OWASP is the Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL), which aims to integrate security practices into every phase of the software development process.
Key Principles of OWASP SDL:
- Start Early: Security considerations should be addressed from the beginning of the development process.
- Risk-Based Approach: Identify and prioritize security risks based on their potential impact.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement mechanisms to continuously monitor and assess security throughout the development lifecycle.
- Educate and Train: Provide training to developers on secure coding practices and common vulnerabilities.
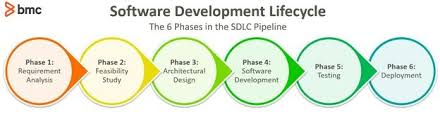
Phases of OWASP SDL:
The OWASP SDL consists of several phases that guide developers in building secure software:
- Requirements: Define security requirements and constraints early in the project.
- Design: Incorporate security controls into the design phase to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Implementation: Follow secure coding practices and conduct code reviews to identify and fix security issues.
- Testing: Perform thorough security testing, including penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, to identify weaknesses.
- Release/Deployment: Ensure that security controls are in place before deploying the application to production environments.
- Maintenance: Continuously monitor and update the application to address new security threats and vulnerabilities.
Benefits of OWASP SDL:
The implementation of OWASP SDL offers several benefits, including:
- Better Security Posture: By integrating security from the start, developers can build more secure applications.
- Cost Savings: Addressing security issues early in the development process can help prevent costly fixes later on.
- Mitigation of Risks: Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities proactively reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks.
In conclusion, adopting OWASP SDL principles can significantly enhance the security of software applications. By following a structured approach that incorporates security throughout the development lifecycle, organizations can build more resilient and secure systems that protect both their data and users.
Understanding OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL): Key FAQs and Insights
- What is OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL)?
- Why is OWASP SDL important in software development?
- What are the key principles of OWASP SDL?
- How does OWASP SDL help improve software security?
- What are the phases of OWASP SDL and their significance?
- How can developers integrate security practices into each phase of the SDLC?
- What are the benefits of implementing OWASP SDL in an organization?
- Are there any tools or resources available to support the implementation of OWASP SDL?
What is OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL)?
The OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) is a structured approach designed by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) to integrate security practices into every phase of the software development process. It aims to address security considerations from the early stages of development, prioritize and mitigate risks, continuously monitor security, and educate developers on secure coding practices. By following the OWASP SDL guidelines, organizations can build more secure software applications that are resilient against potential vulnerabilities and cyber threats.
Why is OWASP SDL important in software development?
The OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) is crucial in software development because it integrates security practices at every stage of the development process. By prioritizing security from the beginning, OWASP SDL helps identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities early on, reducing the risk of security breaches and data leaks. Incorporating security measures throughout the software development lifecycle not only enhances the overall security posture of applications but also saves time and resources by addressing issues proactively. OWASP SDL ensures that developers are well-equipped to build secure software that can withstand evolving cyber threats, ultimately safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining user trust.
What are the key principles of OWASP SDL?
One of the frequently asked questions about OWASP SDL revolves around its key principles. The key principles of OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) emphasize starting early with security considerations, adopting a risk-based approach to prioritize vulnerabilities, implementing continuous monitoring mechanisms, and providing education and training to developers on secure coding practices and common vulnerabilities. By adhering to these principles, organizations can integrate security practices into every phase of the software development process, ultimately enhancing the security posture of their applications and mitigating potential risks effectively.
How does OWASP SDL help improve software security?
The OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) plays a crucial role in enhancing software security by integrating security practices into every phase of the software development process. OWASP SDL helps improve software security by ensuring that security considerations are addressed from the early stages of development, identifying and prioritizing security risks based on their potential impact, implementing continuous monitoring mechanisms to assess security throughout the lifecycle, providing education and training on secure coding practices, and guiding developers through a structured approach that incorporates security controls into design, implementation, testing, release/deployment, and maintenance phases. By following OWASP SDL principles, organizations can build more secure applications, reduce vulnerabilities, mitigate risks of data breaches and cyber attacks, and ultimately enhance the overall security posture of their software products.
What are the phases of OWASP SDL and their significance?
The phases of OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) play a crucial role in ensuring the security of software applications. Each phase, including requirements, design, implementation, testing, release/deployment, and maintenance, has its own significance in integrating security practices throughout the development process. By defining security requirements early on, incorporating security controls into the design phase, following secure coding practices during implementation, conducting thorough security testing, ensuring secure deployment, and maintaining ongoing security measures post-launch, organizations can build robust and resilient applications that are better protected against potential cyber threats. Embracing these phases helps developers identify and address security vulnerabilities proactively, ultimately leading to safer software products for users.
How can developers integrate security practices into each phase of the SDLC?
Developers can integrate security practices into each phase of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) by following a structured approach outlined by OWASP SDL principles. Starting from the requirements phase, developers can define security requirements early on and incorporate security controls into the design phase to mitigate potential vulnerabilities. During implementation, following secure coding practices and conducting code reviews help identify and fix security issues. Thorough security testing, including penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, in the testing phase ensures that weaknesses are identified before deployment. By continuously monitoring and updating the application in the maintenance phase, developers can address new security threats and vulnerabilities effectively. This holistic approach ensures that security is ingrained in every aspect of the SDLC, leading to the development of more secure and resilient software applications.
What are the benefits of implementing OWASP SDL in an organization?
Implementing the OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) in an organization offers a multitude of benefits. By integrating security practices from the early stages of software development, organizations can enhance their overall security posture. This proactive approach helps in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they become significant risks, ultimately leading to a reduction in potential data breaches and cyber attacks. Additionally, implementing OWASP SDL can result in cost savings by preventing expensive fixes that may be required if security issues are discovered later in the development process. Overall, embracing OWASP SDL principles can help organizations build more secure and resilient software applications that protect both their data and their reputation.
Are there any tools or resources available to support the implementation of OWASP SDL?
Many tools and resources are available to support the implementation of OWASP Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL). The OWASP community provides a variety of open-source tools, guidelines, and best practices that can help developers integrate security into their development processes. Tools such as OWASP ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy), Dependency-Check, and Code Dx offer functionalities for vulnerability scanning, dependency analysis, and code review to identify and address security issues early on. Additionally, OWASP provides comprehensive documentation, training materials, and reference guides to assist organizations in implementing SDL effectively. By leveraging these tools and resources, developers can enhance the security of their software applications and mitigate potential risks associated with vulnerabilities.