Optimizing Real Estate Projects with Property Development Software
The Role of Property Development Software in Streamlining Real Estate Projects
In the fast-paced world of real estate development, efficiency and precision are key to success. Property development software plays a crucial role in streamlining and optimizing various aspects of real estate projects, from planning and design to construction and management.
Enhanced Planning and Design
Property development software offers advanced tools for architects, engineers, and designers to create detailed plans and designs for buildings and developments. Through 3D modeling, visualization, and simulation features, stakeholders can better understand the project scope and make informed decisions early in the process.
Project Management and Collaboration
Effective project management is essential for the success of any real estate development venture. Property development software enables project managers to track progress, allocate resources efficiently, manage budgets, and communicate with team members in real-time. Collaboration tools facilitate seamless communication among stakeholders, leading to improved coordination and faster decision-making.
Cost Estimation and Analysis
Accurate cost estimation is critical for project feasibility assessment and budget planning. Property development software offers robust features for cost estimation based on materials, labor, equipment, and other factors. Additionally, advanced analytics tools allow developers to analyze different scenarios and optimize costs while maintaining quality standards.
Risk Mitigation and Compliance
Real estate projects are subject to various risks related to regulatory compliance, environmental factors, market conditions, etc. Property development software helps developers identify potential risks early on through risk assessment tools. By ensuring compliance with regulations and standards throughout the project lifecycle, developers can mitigate risks effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, property development software plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, mitigating risks, and improving collaboration in real estate projects. By leveraging the power of technology through specialized software solutions, developers can streamline their processes and achieve successful outcomes in an increasingly competitive industry.
8 Common Questions About Property Development Software: Features, Benefits, and More
- What is property development software?
- How can property development software help in project planning and design?
- What features are typically included in property development software?
- How does property development software assist in project management and collaboration?
- Can property development software help with cost estimation and budgeting?
- What role does property development software play in risk mitigation and compliance?
- Is property development software customizable to suit different project requirements?
- What are the key benefits of using property development software for real estate projects?
What is property development software?
Property development software is a specialized tool designed to streamline and optimize various aspects of real estate projects, from initial planning and design to construction and management. This software offers a range of features such as 3D modeling, project management tools, cost estimation capabilities, and risk assessment functionalities. It allows stakeholders, including architects, engineers, project managers, and developers, to collaborate effectively, make informed decisions, and ensure compliance with regulations throughout the project lifecycle. Property development software plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, mitigating risks, and improving overall project outcomes in the dynamic and competitive real estate development industry.
How can property development software help in project planning and design?
Property development software offers valuable tools and features that significantly aid in project planning and design within the real estate industry. By utilizing advanced 3D modeling, visualization, and simulation capabilities, this software enables architects, engineers, and designers to create detailed plans and designs with precision and efficiency. Stakeholders can visualize the project layout, analyze spatial relationships, and make informed decisions early in the planning phase. The software’s collaborative features facilitate seamless communication among team members, ensuring that all stakeholders are on the same page throughout the design process. Overall, property development software enhances project planning and design by providing a comprehensive platform for visualizing concepts, optimizing layouts, and fostering effective collaboration among project teams.
What features are typically included in property development software?
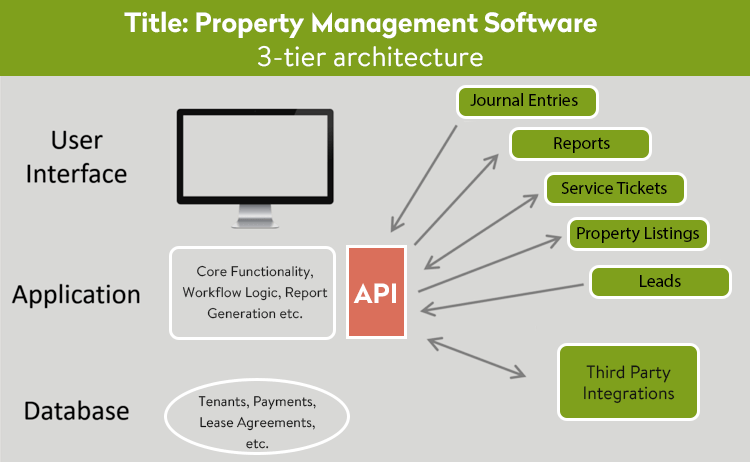
Property development software typically includes a range of features designed to streamline and optimize various aspects of real estate projects. Common features found in such software include advanced tools for planning and design, such as 3D modeling and visualization capabilities. Project management functionalities allow users to track progress, allocate resources efficiently, manage budgets, and facilitate collaboration among team members. Cost estimation and analysis tools help developers assess project feasibility and optimize costs based on materials, labor, and other factors. Additionally, risk mitigation features aid in identifying and addressing potential risks related to compliance, environmental factors, and market conditions. Overall, property development software offers a comprehensive suite of tools to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, mitigate risks, and improve project outcomes in the real estate development industry.
How does property development software assist in project management and collaboration?
Property development software plays a crucial role in facilitating project management and collaboration in real estate development projects. By providing advanced tools for tracking progress, allocating resources, managing budgets, and enabling real-time communication among team members, property development software enhances efficiency and coordination throughout the project lifecycle. Project managers can leverage features such as task assignment, milestone tracking, document sharing, and communication channels to ensure seamless collaboration among stakeholders. Additionally, the software enables stakeholders to access project data and updates from anywhere, promoting transparency and informed decision-making. Overall, property development software streamlines project management processes and fosters effective collaboration among team members to drive successful outcomes in real estate projects.
Can property development software help with cost estimation and budgeting?
Property development software is a valuable tool that can significantly aid in cost estimation and budgeting for real estate projects. By utilizing advanced features and analytics tools, property development software enables developers to accurately estimate costs based on various factors such as materials, labor, equipment, and market conditions. This software allows for detailed analysis of project expenses and helps in creating realistic budgets that align with project requirements. With the ability to simulate different scenarios and optimize costs while maintaining quality standards, property development software plays a crucial role in ensuring financial feasibility and successful outcomes for real estate developments.
What role does property development software play in risk mitigation and compliance?
Property development software plays a crucial role in risk mitigation and compliance by providing developers with tools to identify, assess, and address potential risks throughout the project lifecycle. By integrating features such as risk assessment tools, regulatory compliance checks, and real-time monitoring capabilities, property development software helps developers proactively manage risks related to regulatory requirements, environmental factors, market conditions, and other variables. By ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulations, developers can minimize legal liabilities, avoid costly delays, and maintain project integrity, ultimately enhancing the overall success and sustainability of real estate projects.
Is property development software customizable to suit different project requirements?
Property development software often offers a high degree of customization to accommodate diverse project requirements. Developers can tailor the software to align with specific project needs, such as varying scales, property types, and stakeholder preferences. Customization options may include adjusting workflows, templates, reports, and features to enhance efficiency and address unique challenges. By allowing flexibility in configuration and adaptation, property development software empowers users to optimize their processes and achieve tailored solutions that best fit their project goals and specifications.
What are the key benefits of using property development software for real estate projects?
Property development software offers a multitude of key benefits for real estate projects. Firstly, it enhances efficiency by providing advanced tools for planning, design, and project management, leading to streamlined processes and faster decision-making. Secondly, it improves collaboration among stakeholders through real-time communication and data sharing, fostering better coordination and teamwork. Additionally, the software enables accurate cost estimation and analysis, helping developers optimize budgets and resources effectively. Moreover, property development software aids in risk mitigation by identifying potential risks early on and ensuring compliance with regulations throughout the project lifecycle. Overall, the use of property development software results in increased productivity, reduced costs, minimized risks, and ultimately contributes to the successful execution of real estate projects.