Exploring the Significance of SDLC in Software Testing Practices
The Importance of SDLC in Software Testing
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a crucial process that outlines the various stages involved in developing software applications. In the realm of software testing, understanding SDLC is essential for ensuring the quality and reliability of software products.
Phases of SDLC in Software Testing
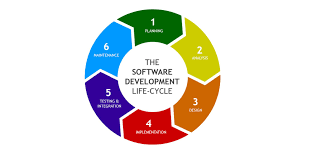
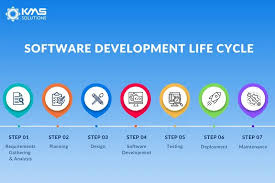
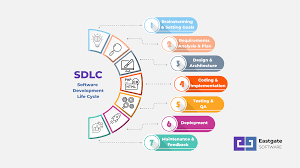
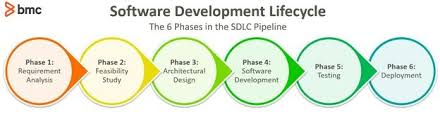
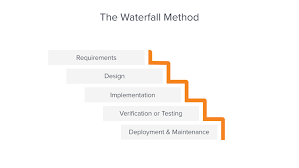
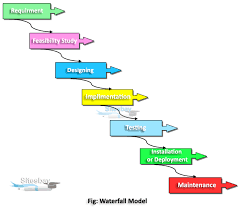
SDLC consists of several phases, each playing a vital role in the development and testing of software:
- Requirement Analysis: This phase involves gathering and analyzing requirements from stakeholders to understand the scope of the project.
- Design: In this phase, the system architecture and design are planned based on the gathered requirements.
- Development: The actual coding and implementation of the software take place in this phase.
- Testing: Software testing is a critical phase where various testing techniques are applied to ensure that the software meets quality standards.
- Deployment: Once testing is complete, the software is deployed for use by end-users.
- Maintenance: Ongoing maintenance and support are provided to address any issues that may arise post-deployment.
The Role of Testing in SDLC
In SDLC, testing plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the software meets specified requirements and functions as intended. Different types of testing, such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing, are conducted at various stages to identify defects and ensure quality.
Benefits of Following SDLC in Software Testing
Adhering to SDLC principles offers several benefits for software development and testing processes:
- Better Quality Assurance: By following a structured approach to development and testing, organizations can enhance the quality of their software products.
- Risk Mitigation: SDLC helps identify potential risks early in the development cycle, allowing teams to address them proactively.
- Cost Efficiency: By detecting defects early on through rigorous testing practices, organizations can save costs associated with fixing issues post-deployment.
- Timely Delivery: Following a well-defined SDLC framework ensures that projects are completed within stipulated timelines by streamlining development and testing processes.
In conclusion, understanding SDLC is essential for successful software testing. By following a structured approach to development and incorporating robust testing practices at each stage, organizations can deliver high-quality software products that meet user expectations.
9 Key Advantages of Implementing SDLC in Software Testing
- Structured approach to software development
- Early identification of potential risks
- Enhanced quality assurance through rigorous testing practices
- Improved project management and planning
- Cost-effective by detecting defects early in the cycle
- Timely delivery of software projects
- Clear documentation and traceability of requirements
- Facilitates collaboration among development and testing teams
- Supports scalability and adaptability of software applications
7 Drawbacks of the Software Development Life Cycle in Testing: Rigid, Costly, and More
- Rigid Process
- Time-Consuming
- Costly
- Complexity
- Resource Intensive
- Potential for Overhead
- Limited Agility
Structured approach to software development
A significant advantage of SDLC in software testing is its structured approach to software development. By following a systematic and well-defined process, teams can ensure that all necessary steps, from requirements gathering to deployment, are executed in an organized manner. This structured approach helps in reducing errors, improving efficiency, and enhancing overall project management. It allows for better planning, tracking progress, and ensuring that the final product meets quality standards. Ultimately, the structured approach of SDLC contributes to the successful delivery of reliable and high-quality software solutions.
Early identification of potential risks
One significant advantage of following the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in software testing is the early identification of potential risks. By systematically planning and executing testing activities at different stages of the development process, teams can proactively uncover and address risks before they escalate into critical issues. This proactive approach not only helps in mitigating potential threats to the software’s quality and functionality but also contributes to overall project success by minimizing the impact of unforeseen challenges.
Enhanced quality assurance through rigorous testing practices
Enhanced quality assurance through rigorous testing practices is a significant benefit of following the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in software testing. By incorporating thorough testing at each stage of the development process, organizations can identify and rectify defects early on, ensuring that the software meets specified requirements and functions as intended. This proactive approach to quality assurance not only helps in delivering high-quality software products but also instills confidence in stakeholders regarding the reliability and performance of the final deliverables.
Improved project management and planning
Improved project management and planning is a significant advantage of incorporating SDLC in software testing. By following a structured approach to development, teams can better organize tasks, allocate resources efficiently, and establish clear timelines for each phase of the project. This leads to enhanced coordination among team members, improved communication with stakeholders, and better risk management throughout the software development life cycle. With a well-defined plan in place, project managers can mitigate potential delays and ensure that projects are delivered on time and within budget, ultimately leading to greater success in software testing endeavors.
Cost-effective by detecting defects early in the cycle
One significant advantage of following the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in software testing is its cost-effectiveness. By detecting defects early in the development cycle, organizations can save substantial costs associated with fixing issues later in the process or post-deployment. Identifying and addressing defects at an early stage not only minimizes the resources required for rectification but also reduces the potential impact on project timelines and budgets. This proactive approach to defect detection and resolution contributes to overall cost savings and ensures that software products are delivered efficiently and within budget constraints.
Timely delivery of software projects
Adhering to the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) framework in software testing ensures the timely delivery of software projects. By following a structured approach that includes defined phases for development and testing, organizations can streamline their processes and effectively manage project timelines. This proactive approach allows teams to identify potential bottlenecks early on, address issues promptly, and ensure that projects are completed within the specified deadlines. Ultimately, the emphasis on timely delivery enabled by SDLC contributes to increased efficiency, client satisfaction, and overall project success.
Clear documentation and traceability of requirements
Clear documentation and traceability of requirements is a significant advantage of SDLC in software testing. By documenting all requirements at the beginning of the development process and tracing them throughout each phase, teams can ensure that the final product aligns closely with stakeholder expectations. This practice not only helps in understanding the scope of the project but also facilitates effective communication among team members. Additionally, clear documentation and traceability enable easier identification of potential issues or discrepancies, allowing for timely resolution and ensuring that the software meets all specified requirements.
Facilitates collaboration among development and testing teams
Facilitating collaboration among development and testing teams is a significant advantage of following the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in software testing. By integrating testing activities throughout the development process, SDLC promotes communication and cooperation between developers and testers. This collaborative approach allows for early identification and resolution of issues, ensures alignment on project goals, and fosters a shared understanding of the software requirements. Ultimately, this teamwork leads to improved product quality, faster delivery cycles, and more efficient problem-solving processes within the development and testing teams.
Supports scalability and adaptability of software applications
One significant advantage of following the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in software testing is that it supports the scalability and adaptability of software applications. By adhering to a structured development process, organizations can design software with scalability in mind, allowing applications to easily accommodate growth and increased demands. Additionally, SDLC enables teams to adapt and make changes to software applications efficiently, ensuring that they remain relevant and effective in a dynamic business environment. This proactive approach to development and testing under SDLC helps organizations build robust and flexible software solutions that can evolve alongside changing business requirements.
Rigid Process
One significant drawback of SDLC in software testing is its perceived rigidity, which can hinder adaptability to evolving project requirements. The structured nature of SDLC may impose constraints on accommodating changes during the development process, potentially leading to delays or inefficiencies in responding to new project demands. This rigidity can limit the flexibility needed to address shifting priorities or emerging market trends, ultimately impacting the agility and responsiveness of the software development and testing processes.
Time-Consuming
One significant drawback of following the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in software testing is its time-consuming nature. Adhering to all the phases of SDLC, which include comprehensive testing, can lead to extended development cycles. The thorough testing processes involved in SDLC, while essential for ensuring quality and reliability, may require additional time and resources, potentially delaying the overall project timeline. This prolonged development cycle could pose challenges for meeting tight deadlines or responding quickly to changing market demands.
Costly
One significant drawback of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in software testing is its cost implications. The implementation of a comprehensive SDLC framework with extensive testing procedures can significantly escalate project costs. The resources required for thorough testing activities, such as test planning, execution, and defect resolution, can contribute to budget overruns, especially for organizations with limited financial resources. Balancing the need for rigorous testing to ensure software quality with cost considerations remains a challenge in SDLC implementation.
Complexity
The con of SDLC in software testing lies in its inherent complexity. The structured framework of SDLC, while beneficial for ensuring thorough development and testing processes, can also introduce challenges in managing and coordinating the various stages effectively. The intricate interplay between requirements gathering, design, development, and testing phases may result in increased complexity for project managers and teams. Balancing the need for comprehensive testing with the demands of meeting project timelines within a structured SDLC framework can be a daunting task, requiring careful planning and coordination to navigate the complexities inherent in the software development life cycle.
Resource Intensive
One significant drawback of SDLC in software testing is its resource-intensive nature. Implementing SDLC effectively demands dedicated resources for each phase of the process, from requirements analysis to deployment and maintenance. This allocation of resources can strain the team’s capacity and budget, as it requires substantial time, effort, and financial investments to ensure that each stage is executed efficiently. The need for specialized skills, tools, and personnel at every phase of SDLC can pose challenges for organizations with limited resources, potentially impacting project timelines and overall cost-effectiveness.
Potential for Overhead
In software testing, one significant con of strictly following the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) model is the potential for overhead. While SDLC aims to provide a structured framework for software development and testing, there are instances where adhering rigorously to its guidelines can lead to unnecessary administrative tasks and excessive documentation. This overhead can consume valuable time and resources, diverting focus away from actual testing activities and potentially slowing down the overall development process. It is essential for organizations to strike a balance between adhering to SDLC principles and avoiding excessive bureaucracy to ensure efficient and effective software testing practices.
Limited Agility
In software testing, a significant drawback of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is its limited agility. The sequential progression of SDLC phases can impede the swift implementation of changes or iterations necessary in agile development environments. In today’s fast-paced and dynamic industry, where flexibility and adaptability are paramount, the rigid structure of SDLC may restrict the ability to respond quickly to evolving requirements or market demands. This limitation highlights the challenge of balancing structured processes with the need for agility in software development and testing practices.