Unlocking Speed and Flexibility: The Power of Rapid Application Development
The Power of Rapid Application Development
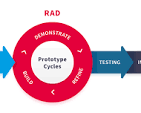
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a software development approach that prioritizes speed and flexibility in creating applications. In today’s fast-paced digital world, the ability to quickly develop and deploy applications can give businesses a competitive edge.
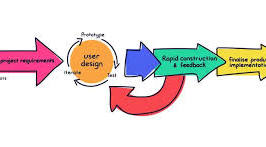
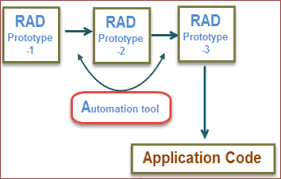
One of the key benefits of RAD is its iterative and incremental nature. Instead of following a linear development process, RAD allows for quick prototyping and feedback loops. This means that changes can be implemented rapidly based on user input, resulting in faster delivery of functional software.
RAD also encourages collaboration between developers, designers, and end-users. By involving stakeholders throughout the development process, RAD ensures that the final product meets the needs and expectations of its intended users.
Another advantage of RAD is its focus on reusability. Developers can leverage existing components and frameworks to accelerate development without compromising quality. This not only speeds up the development process but also reduces costs associated with building applications from scratch.
Furthermore, RAD promotes a more flexible approach to project management. By breaking down projects into smaller modules or features, teams can prioritize tasks based on their importance and complexity. This allows for greater adaptability to changing requirements and market conditions.
In conclusion, Rapid Application Development offers a streamlined and efficient way to create software applications in a fast-paced environment. By emphasizing collaboration, reusability, and flexibility, RAD empowers businesses to innovate quickly and stay ahead of the competition.
5 Essential Tips for Accelerating Application Development Success
- Define clear objectives and requirements before starting development.
- Use rapid prototyping to quickly visualize ideas and gather feedback.
- Prioritize essential features to deliver a minimum viable product (MVP) faster.
- Implement agile development practices for flexibility and adaptability.
- Regularly test and iterate on the application to improve functionality and user experience.
Define clear objectives and requirements before starting development.
Before diving into rapid application development, it is crucial to define clear objectives and requirements. By establishing a solid foundation at the outset, developers can ensure that the project stays on track and meets the desired outcomes. Clear objectives help align the team’s efforts and provide a roadmap for development, while well-defined requirements serve as a guide for implementing features that are essential to the success of the application. Taking the time to clarify objectives and requirements upfront can prevent costly rework later on and ultimately lead to a more efficient and successful development process.
Use rapid prototyping to quickly visualize ideas and gather feedback.
Using rapid prototyping is a valuable tip in the realm of rapid application development as it allows developers to swiftly bring ideas to life and gather essential feedback. By creating prototypes that provide a visual representation of the proposed application, stakeholders can better understand the concept and provide input early in the development process. This iterative approach not only accelerates the design phase but also ensures that the final product aligns with user expectations and requirements, ultimately leading to a more successful and user-friendly application.
Prioritize essential features to deliver a minimum viable product (MVP) faster.
When adopting Rapid Application Development, it is crucial to prioritize essential features to deliver a minimum viable product (MVP) faster. By focusing on the core functionalities that provide the most value to users, developers can streamline the development process and get a functional product into the hands of users sooner. This approach not only accelerates time-to-market but also allows for early feedback and validation, enabling teams to make informed decisions and iterate on the product efficiently.
Implement agile development practices for flexibility and adaptability.
Implementing agile development practices is essential for leveraging the benefits of rapid application development. By embracing agile methodologies, such as iterative development, continuous feedback, and adaptive planning, teams can enhance flexibility and adaptability in their software projects. Agile allows for quick adjustments to changing requirements and market conditions, ensuring that the final product meets user needs effectively. This approach promotes collaboration, transparency, and a customer-centric mindset, ultimately leading to the successful delivery of high-quality applications within shorter timeframes.
Regularly test and iterate on the application to improve functionality and user experience.
Regularly testing and iterating on the application is crucial in enhancing its functionality and user experience. By conducting frequent tests and gathering feedback from users, developers can identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to ensure a seamless and user-friendly application. This iterative process not only helps in fixing bugs and issues but also allows for continuous enhancement of features based on user preferences and behavior. Ultimately, prioritizing regular testing and iteration leads to a more refined and efficient application that meets the evolving needs of its users.