Unlocking Success with Extreme Programming (XP) Methodology
Exploring Extreme Programming (XP)
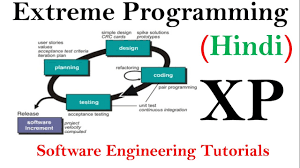
Extreme Programming (XP) is a software development methodology that aims to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. It is based on a set of values, principles, and practices that emphasize collaboration, feedback, simplicity, and flexibility.
Key Principles of XP:
- Communication: XP promotes frequent communication among team members, customers, and stakeholders to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding project goals and progress.
- Simplicity: XP advocates for keeping things simple by focusing on the most essential features and avoiding unnecessary complexity in the codebase.
- Feedback: XP emphasizes the importance of receiving feedback early and often through practices like continuous integration, testing, and regular reviews.
- Courage: XP encourages team members to take risks, experiment with new ideas, and address challenges proactively.
- Respect: XP values mutual respect among team members, fostering a positive work environment where everyone’s contributions are acknowledged and appreciated.
Core Practices of XP:
- Pair Programming: Two programmers work together at one computer, collaborating on code design, implementation, and problem-solving.
- Test-Driven Development (TDD): Developers write automated tests before writing code to ensure that the code meets specified requirements.
- Continuous Integration: Code changes are integrated into a shared repository frequently to detect integration issues early.
- Sustainable Pace: Teams maintain a sustainable work pace to prevent burnout and ensure long-term productivity.
- Coding Standards: Consistent coding standards are enforced to promote readability, maintainability, and collaboration within the team.
In conclusion, Extreme Programming (XP) offers a disciplined approach to software development that prioritizes customer satisfaction, teamwork, adaptability, and continuous improvement. By embracing its values and practices, teams can deliver high-quality software efficiently while responding effectively to changing requirements in today’s dynamic business environment.
8 Key Benefits of Extreme Programming: Enhancing Communication, Simplicity, and Code Quality
- Promotes frequent communication among team members
- Emphasizes simplicity in code design and implementation
- Encourages receiving feedback early and often
- Fosters a culture of experimentation and risk-taking
- Values mutual respect among team members
- Enhances collaboration through pair programming
- Ensures code quality through test-driven development (TDD)
- Supports sustainable work pace to prevent burnout
Challenges of Extreme Programming: Team Dynamics, Documentation Concerns, and Cultural Shifts
- High dependency on strong teamwork and collaboration may be challenging in environments with individualistic team members.
- Emphasis on simplicity and flexibility could lead to potential lack of documentation and long-term maintainability concerns.
- Strict adherence to XP practices may require a significant cultural shift within organizations accustomed to traditional development methodologies.
Promotes frequent communication among team members
One significant advantage of Extreme Programming (XP) is its promotion of frequent communication among team members. By encouraging regular and open dialogue, XP facilitates a collaborative environment where team members can share ideas, clarify requirements, and address any challenges effectively. This emphasis on communication helps improve team cohesion, enhances understanding of project goals, and ensures that everyone is aligned towards achieving the desired outcomes. Ultimately, the practice of promoting frequent communication in XP leads to better coordination, increased productivity, and improved overall project success.
Emphasizes simplicity in code design and implementation
Extreme Programming (XP) stands out for its emphasis on simplicity in code design and implementation. By prioritizing straightforward and clear solutions, XP promotes code that is easier to understand, maintain, and extend. This approach not only enhances the readability of the codebase but also reduces the likelihood of introducing bugs or errors. Embracing simplicity in code design through XP allows teams to deliver high-quality software efficiently while fostering a collaborative and productive development environment.
Encourages receiving feedback early and often
One of the key advantages of Extreme Programming (XP) is its emphasis on encouraging the practice of receiving feedback early and often. By soliciting feedback at various stages of the development process, teams can identify potential issues, validate assumptions, and make necessary adjustments promptly. This proactive approach not only helps in improving the quality of the software but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration within the team. Ultimately, by incorporating regular feedback loops into their workflow, XP teams can ensure that they are building products that meet customer needs effectively and efficiently.
Fosters a culture of experimentation and risk-taking
Extreme Programming (XP) fosters a culture of experimentation and risk-taking by encouraging team members to explore new ideas, try out innovative approaches, and address challenges proactively. This pro of XP empowers developers to step out of their comfort zones, take calculated risks, and learn from both successes and failures. By embracing a mindset that values experimentation and continuous improvement, XP teams can drive innovation, discover creative solutions to complex problems, and adapt swiftly to changing requirements in the software development process.
Values mutual respect among team members
In Extreme Programming (XP), one of the key advantages is its emphasis on valuing mutual respect among team members. By fostering an environment where every team member’s contributions are acknowledged and appreciated, XP promotes a positive and collaborative work culture. This focus on mutual respect not only boosts morale and team cohesion but also encourages open communication, idea-sharing, and a sense of belonging within the team. Ultimately, by prioritizing mutual respect, XP helps create a supportive and inclusive atmosphere where individuals feel valued and motivated to work together towards shared goals.
Enhances collaboration through pair programming
Pair programming, a core practice of Extreme Programming (XP), enhances collaboration by fostering real-time communication and knowledge sharing between two developers working together at a single workstation. This approach not only results in higher code quality and fewer defects but also promotes teamwork, creativity, and mutual learning. By combining the skills and perspectives of two individuals, pair programming in XP encourages continuous feedback, problem-solving, and collective ownership of the codebase, ultimately leading to improved productivity and a stronger sense of camaraderie within the development team.
Ensures code quality through test-driven development (TDD)
One significant advantage of Extreme Programming (XP) is its emphasis on ensuring code quality through Test-Driven Development (TDD). With TDD, developers write automated tests before writing the actual code, allowing them to define clear requirements and expectations for the functionality of the software. By following this practice, XP teams can detect errors early in the development process, maintain a high standard of code quality, and create a more robust and reliable software product.
Supports sustainable work pace to prevent burnout
Extreme Programming (XP) promotes a sustainable work pace to prevent burnout among team members. By emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy balance between work and personal well-being, XP encourages teams to avoid overworking and prioritize sustainable productivity. This approach not only fosters a positive work environment but also helps ensure that team members can consistently deliver high-quality results without compromising their mental and physical health.
High dependency on strong teamwork and collaboration may be challenging in environments with individualistic team members.
In Extreme Programming (XP), one significant drawback is its high dependency on strong teamwork and collaboration, which can be challenging in environments where team members lean towards individualism. In such settings, getting everyone to actively engage in pair programming, continuous communication, and collective decision-making processes may prove difficult. The success of XP relies heavily on the synergy and cooperation among team members, making it crucial for individualistic team members to adapt their working style to prioritize group dynamics over personal preferences. Failure to foster a collaborative environment can hinder the effectiveness of XP practices and impede the project’s overall success.
Emphasis on simplicity and flexibility could lead to potential lack of documentation and long-term maintainability concerns.
In Extreme Programming (XP), the emphasis on simplicity and flexibility, while beneficial for rapid development and adaptability, can present a con in terms of documentation and long-term maintainability. Due to the focus on writing just enough code to fulfill immediate requirements, there may be a tendency to prioritize working software over comprehensive documentation. This approach could lead to challenges in understanding the codebase for future maintenance or new team members. Ensuring proper documentation practices and balancing simplicity with sufficient explanatory materials are crucial to mitigate potential issues related to long-term maintainability in XP projects.
Strict adherence to XP practices may require a significant cultural shift within organizations accustomed to traditional development methodologies.
Adhering strictly to Extreme Programming (XP) practices may present a challenge due to the potential need for a significant cultural shift within organizations accustomed to traditional development methodologies. Transitioning to XP requires embracing values such as collaboration, continuous feedback, and adaptability, which may differ from the hierarchical structures and rigid processes commonly found in traditional environments. This cultural shift can be disruptive and may require time, effort, and buy-in from all levels of the organization to successfully integrate XP practices and realize their benefits.