Mastering the Iterative SDLC Approach for Agile Software Development
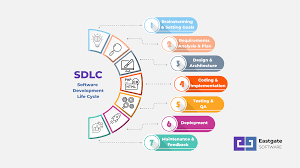
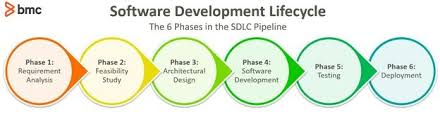
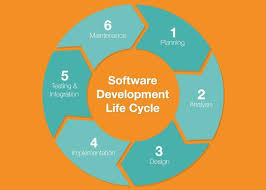
The Iterative Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
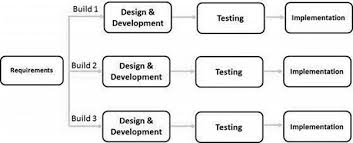
Iterative software development is a methodology that breaks down the software development process into smaller cycles or iterations. Each iteration involves planning, designing, implementing, testing, and reviewing a specific set of features or functionalities.
The iterative approach allows for flexibility and adaptability throughout the development process. Instead of waiting until the end to release a final product, iterative SDLC enables developers to deliver working software in incremental stages.
Key Characteristics of Iterative SDLC:
- Flexibility: The ability to make changes and improvements at any stage of development.
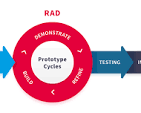
- Rapid Prototyping: Creating prototypes early in the process to gather feedback and make adjustments.
- Continuous Testing: Testing is integrated throughout each iteration to identify and address issues promptly.
- Client Involvement: Clients are actively engaged in providing feedback and shaping the direction of the project.
Benefits of Using an Iterative SDLC Approach:
- Enhanced Collaboration: Team members collaborate closely throughout the development process, leading to improved communication and teamwork.
- Reduced Risk: Identifying and addressing issues early on helps mitigate risks associated with developing complex software.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Delivering functional components incrementally can lead to quicker deployment of key features.
- Better Adaptability: The iterative approach allows for changes based on evolving requirements or market conditions.
In conclusion, the iterative software development life cycle offers a dynamic and efficient way to build high-quality software products. By embracing flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement, teams can deliver value to clients while adapting to changing needs in today’s fast-paced technological landscape.
9 Advantages of Iterative SDLC: Flexibility, Feedback, and Faster Results
- Flexibility to incorporate changes at any stage of development.
- Early and continuous feedback from stakeholders leads to improved outcomes.
- Reduces risks by identifying and addressing issues early in the process.
- Enhanced collaboration among team members fosters better communication and teamwork.
- Allows for rapid prototyping to test ideas and concepts quickly.
- Faster time-to-market with incremental delivery of working software components.
- Client involvement throughout the process ensures alignment with expectations and requirements.
- Better adaptability to changing market conditions or evolving project needs.
- Continuous testing and refinement lead to higher quality end products.
Challenges of Iterative SDLC: Managing Complexity, Scope Creep, and Coordination
- Increased complexity due to managing multiple iterations simultaneously
- Potential for scope creep as requirements may evolve with each iteration
- Higher coordination effort required to ensure all team members are aligned
- Difficulty in estimating project timelines accurately with iterative cycles
- Risk of overlooking critical features or dependencies in the incremental delivery process
- Possibility of increased costs if changes are frequent and substantial
- Challenges in maintaining consistency and coherence across multiple iterations
Flexibility to incorporate changes at any stage of development.
The flexibility offered by the iterative software development life cycle allows teams to seamlessly incorporate changes at any stage of the development process. This adaptability empowers developers to respond to evolving requirements, feedback, or market trends without disrupting the entire project timeline. By embracing this pro of iterative SDLC, teams can ensure that their software remains aligned with stakeholders’ needs and expectations, ultimately leading to a more successful and customer-centric end product.
Early and continuous feedback from stakeholders leads to improved outcomes.
Early and continuous feedback from stakeholders is a crucial advantage of the iterative software development life cycle (SDLC). By involving stakeholders throughout the development process, teams can gather valuable insights, identify potential issues, and make necessary adjustments promptly. This ongoing feedback loop ensures that the final product aligns closely with stakeholder expectations and requirements, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and higher satisfaction levels. The ability to incorporate stakeholder input early on in the development cycle enhances collaboration, fosters transparency, and increases the likelihood of delivering a successful software solution that meets the needs of all parties involved.
Reduces risks by identifying and addressing issues early in the process.
One significant advantage of the iterative software development life cycle is its ability to reduce risks by proactively identifying and addressing issues early in the process. By breaking down the development into smaller iterations, teams can quickly detect potential problems and make necessary adjustments before they escalate. This proactive approach not only minimizes the chances of major setbacks but also ensures a smoother and more efficient development process, ultimately leading to a higher quality end product.
Enhanced collaboration among team members fosters better communication and teamwork.
Enhanced collaboration among team members in an iterative software development life cycle (SDLC) fosters better communication and teamwork. By working closely together throughout the development process, team members can share ideas, provide feedback, and address challenges collaboratively. This increased interaction not only improves the quality of the final product but also enhances the overall efficiency of the project. Team members can leverage their diverse skills and expertise to overcome obstacles and achieve common goals, leading to a more cohesive and productive work environment.
Allows for rapid prototyping to test ideas and concepts quickly.
One of the key advantages of using an iterative software development life cycle is its ability to facilitate rapid prototyping, enabling teams to test ideas and concepts swiftly. By creating prototypes early in the process, developers can gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and end-users, allowing for quick validation of design choices and functionalities. This iterative approach not only accelerates the testing phase but also helps identify potential issues or improvements at an early stage, leading to more efficient development and a higher-quality end product.
Faster time-to-market with incremental delivery of working software components.
One significant advantage of the iterative software development life cycle is the faster time-to-market achieved through the incremental delivery of working software components. By breaking down the development process into manageable iterations, teams can deliver functional pieces of the product sooner, allowing for quicker deployment of key features. This approach not only accelerates the overall development timeline but also enables stakeholders to start benefiting from usable software early on, leading to enhanced feedback loops and improved adaptability to changing requirements or market demands.
Client involvement throughout the process ensures alignment with expectations and requirements.
Client involvement throughout the iterative software development life cycle (SDLC) is a crucial benefit that ensures alignment with expectations and requirements. By actively engaging clients in the development process, teams can gather valuable feedback, clarify project goals, and make necessary adjustments early on. This collaborative approach helps build a shared understanding between developers and clients, leading to the delivery of a product that meets or exceeds expectations. It also fosters transparency and trust, ultimately resulting in a successful outcome that aligns closely with the client’s needs and vision.
Better adaptability to changing market conditions or evolving project needs.
The iterative software development life cycle excels in its ability to offer better adaptability to changing market conditions or evolving project needs. By breaking down the development process into manageable iterations, teams can quickly respond to new requirements, feedback, or market trends. This flexibility allows for adjustments to be made throughout the project, ensuring that the final product meets the most up-to-date demands and expectations. Ultimately, this adaptability not only enhances the quality of the software but also increases its relevance and competitiveness in a dynamic business environment.
Continuous testing and refinement lead to higher quality end products.
Continuous testing and refinement in the iterative software development life cycle (SDLC) play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of end products. By integrating testing throughout each iteration, developers can identify and address issues promptly, leading to a more robust and reliable final product. This proactive approach not only helps in detecting and resolving defects early on but also allows for ongoing improvements based on feedback and real-world usage. As a result, the iterative SDLC promotes the delivery of higher quality software solutions that meet or exceed user expectations.
Increased complexity due to managing multiple iterations simultaneously
One significant drawback of the iterative software development life cycle is the increased complexity that arises from managing multiple iterations simultaneously. This challenge can be demanding for project managers and team members as they need to coordinate and prioritize tasks across different iterations effectively. Balancing resources, timelines, and dependencies among various ongoing cycles can lead to confusion, potential conflicts, and a higher risk of overlooking critical aspects of the development process. Consequently, this complexity may hinder the overall efficiency and cohesion of the project, potentially impacting its success in meeting deadlines and delivering a cohesive final product.
Potential for scope creep as requirements may evolve with each iteration
One significant drawback of the iterative software development life cycle (SDLC) is the potential for scope creep as requirements may evolve with each iteration. While the flexibility of iterative SDLC allows for changes and improvements, constant modifications to project requirements can lead to an expanding scope that may impact timelines, resources, and overall project success. Managing evolving requirements effectively and establishing clear boundaries are essential to mitigate the risk of scope creep in iterative development processes.
Higher coordination effort required to ensure all team members are aligned
In the iterative software development life cycle, one significant drawback is the higher coordination effort needed to ensure that all team members are aligned. As the development process involves multiple iterations with continuous feedback and adjustments, it becomes crucial for team members to stay synchronized in their efforts. This increased coordination requirement can lead to challenges in communication, potential delays in decision-making, and a higher risk of misalignment among team members. Addressing this con effectively is essential to maintain the efficiency and effectiveness of the iterative SDLC approach.
Difficulty in estimating project timelines accurately with iterative cycles
One significant drawback of the iterative software development life cycle is the challenge of accurately estimating project timelines. Due to the iterative nature of the process, where requirements and features evolve over multiple cycles, predicting the exact time needed to complete a project can be complex. Changes and adjustments made during each iteration can impact the overall timeline, making it difficult for stakeholders to set precise deadlines and expectations. This uncertainty in estimating project timelines can lead to potential delays and challenges in managing resources effectively throughout the development process.
Risk of overlooking critical features or dependencies in the incremental delivery process
One significant drawback of the iterative software development life cycle is the risk of overlooking critical features or dependencies during the incremental delivery process. Since development occurs in smaller iterations, there is a possibility that essential functionalities or interdependencies may not receive adequate attention or consideration in each cycle. This oversight can lead to integration issues, performance bottlenecks, or even project delays if crucial elements are not identified and addressed early on in the development process. It underscores the importance of thorough planning and continuous communication to ensure that all key aspects of the software product are properly accounted for and integrated throughout each iteration.
Possibility of increased costs if changes are frequent and substantial
In the iterative software development life cycle, one significant drawback is the potential for increased costs when changes are frequent and substantial. Each iteration may require adjustments to accommodate new requirements or modifications, leading to additional development time and resources. As a result, the cumulative effect of multiple changes throughout the iterative process can escalate project costs beyond initial estimates. Careful planning and stakeholder communication are essential to mitigate this con and ensure that budget constraints are managed effectively.
Challenges in maintaining consistency and coherence across multiple iterations
One significant challenge of the iterative software development life cycle is maintaining consistency and coherence across multiple iterations. As the development process unfolds in incremental stages, ensuring that all iterations align seamlessly with each other can be complex. Changes made in one iteration may impact previously developed features, leading to potential inconsistencies in the overall product. This challenge requires careful planning, communication, and coordination among team members to maintain a cohesive and unified software solution throughout the iterative SDLC process.