Mastering Magento Ecommerce Development: Building Your Online Store with Power and Precision
The Power of Magento Ecommerce Development
Magento is a powerful and versatile platform for building robust ecommerce websites. With its wide range of features and flexibility, Magento has become one of the most popular choices for businesses looking to establish a strong online presence.
Why Choose Magento for Ecommerce Development?
Here are some key reasons why Magento stands out as a top choice for ecommerce development:
- Scalability: Magento can easily scale to accommodate the growth of your business, whether you are a small startup or a large enterprise.
- Customization: With its modular architecture, Magento allows for extensive customization to meet your specific business needs and branding requirements.
- SEO-Friendly: Magento is designed with search engine optimization (SEO) in mind, making it easier for your online store to rank higher in search engine results.
- Mobile Responsiveness: In today’s mobile-driven world, Magento offers responsive design capabilities to ensure seamless user experience across all devices.
- Rich Features: From product catalog management to secure payment gateways, Magento provides a comprehensive set of features to enhance your ecommerce website’s functionality.
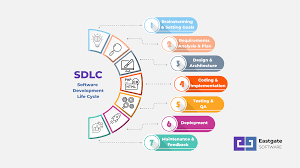
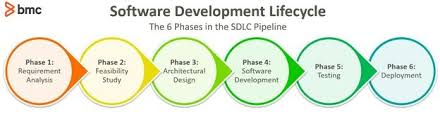
The Process of Magento Ecommerce Development
The process of developing an ecommerce website with Magento typically involves the following steps:
- Planning: Define your goals, target audience, and desired features for the ecommerce site.
- Design: Create a visually appealing and user-friendly design that reflects your brand identity.
- Development: Implement custom functionalities, integrate payment gateways, and optimize performance for seamless user experience.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to ensure that the website functions properly across different devices and browsers.
- Launch & Maintenance: Deploy the website live and continue to monitor performance, make updates, and provide ongoing support as needed.
In Conclusion
Magento ecommerce development offers businesses a powerful platform to create engaging online shopping experiences for their customers. With its flexibility, scalability, and rich feature set, Magento continues to be a top choice for businesses looking to thrive in the competitive world of ecommerce.
8 Essential FAQs About Magento Ecommerce Development: From Features to Finding the Right Developer
- What is Magento ecommerce development?
- How does Magento help businesses create online stores?
- What are the key features of Magento for ecommerce development?
- Is Magento suitable for small businesses or only large enterprises?
- Can Magento be customized to meet specific business needs?
- Does Magento support mobile responsiveness for ecommerce websites?
- What are the SEO capabilities of Magento for improving online visibility?
- How can I find a reliable developer for Magento ecommerce development projects?
What is Magento ecommerce development?
Magento ecommerce development refers to the process of creating online stores and ecommerce websites using the Magento platform. Magento is a popular and powerful open-source ecommerce solution that offers a wide range of features and customization options for businesses looking to establish a strong online presence. With Magento ecommerce development, businesses can build secure, scalable, and feature-rich online stores that provide a seamless shopping experience for customers. From product catalog management to payment gateway integration, Magento ecommerce development enables businesses to create customized and visually appealing online stores that drive sales and enhance customer engagement.
How does Magento help businesses create online stores?
Magento helps businesses create online stores by providing a robust and versatile platform that enables customization, scalability, and rich features. With Magento’s modular architecture, businesses can tailor their online stores to meet specific branding and functionality requirements. The platform’s scalability allows for seamless growth as businesses expand their online presence. Additionally, Magento offers a wide range of features, from product catalog management to secure payment gateways, that enhance the overall shopping experience for customers. Overall, Magento empowers businesses to build engaging and successful online stores that drive growth and profitability.
What are the key features of Magento for ecommerce development?
Magento offers a plethora of key features that make it a top choice for ecommerce development. Some of the standout features include its scalability, allowing businesses to easily expand their online presence as they grow. Magento’s customization capabilities enable businesses to tailor their ecommerce websites to meet specific branding and functionality requirements. The platform’s SEO-friendly design helps improve search engine rankings, while its mobile responsiveness ensures a seamless shopping experience across various devices. Additionally, Magento provides robust features for product catalog management, secure payment gateways, and overall enhanced user experience, making it a comprehensive solution for successful ecommerce development.
Is Magento suitable for small businesses or only large enterprises?
When considering Magento for ecommerce development, a frequently asked question is whether it is suitable for small businesses or only large enterprises. The answer lies in Magento’s flexibility and scalability, making it a viable option for businesses of all sizes. While Magento is robust enough to meet the complex needs of large enterprises with high transaction volumes and extensive product catalogs, it also offers a streamlined version, Magento Open Source (formerly known as Magento Community Edition), which is more budget-friendly and suitable for small to medium-sized businesses. With its modular architecture and customizable features, Magento can be tailored to fit the specific requirements of any business, making it a versatile solution for both small startups and established enterprises looking to establish a strong online presence.
Can Magento be customized to meet specific business needs?
Magento is highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor their ecommerce websites to meet specific needs effectively. With its modular architecture and extensive range of customization options, Magento empowers businesses to create unique online stores that align with their branding, functionality requirements, and target audience preferences. Whether it’s customizing product pages, integrating third-party extensions, or implementing specialized features, Magento provides the flexibility and scalability needed to adapt to diverse business needs seamlessly. By leveraging Magento’s customization capabilities, businesses can create a personalized and optimized ecommerce experience that drives engagement, conversions, and long-term success.
Does Magento support mobile responsiveness for ecommerce websites?
Magento is well-known for its robust support of mobile responsiveness for ecommerce websites. With the increasing trend of mobile shopping, Magento ensures that online stores built on its platform are optimized for mobile devices. This means that Magento ecommerce websites automatically adjust their layout and design to provide a seamless and user-friendly shopping experience on smartphones and tablets. By incorporating responsive design capabilities, Magento empowers businesses to reach a wider audience and cater to the growing number of mobile shoppers, ultimately enhancing customer engagement and driving conversions.
What are the SEO capabilities of Magento for improving online visibility?
Magento offers robust SEO capabilities to enhance online visibility and improve search engine rankings for ecommerce websites. With features such as customizable URLs, meta tags, sitemaps, and rich snippets, Magento provides the tools necessary to optimize website content for search engines. Additionally, Magento’s responsive design and fast loading times contribute to a positive user experience, which is a key factor in SEO rankings. By leveraging Magento’s SEO capabilities effectively, businesses can increase their online visibility and attract more organic traffic to their ecommerce websites.
How can I find a reliable developer for Magento ecommerce development projects?
Finding a reliable developer for Magento ecommerce development projects is crucial for the success of your online business. To ensure you partner with a skilled professional, consider looking for developers with proven experience in Magento development, a strong portfolio showcasing their past projects, and positive client testimonials. Additionally, you can explore online platforms specializing in connecting businesses with qualified developers or seek recommendations from industry peers. Conducting thorough interviews and discussing project requirements in detail can help you assess the developer’s expertise and communication skills, ultimately leading to a successful collaboration on your Magento ecommerce development project.