Mastering the Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) for Efficient Project Delivery
The Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Agile software development has gained popularity in recent years due to its iterative and flexible approach to project management. The Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a methodology that focuses on delivering high-quality software quickly and efficiently through collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
Key Principles of Agile SDLC:
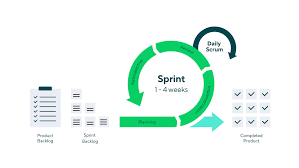
- Iterative Development: Agile SDLC breaks the project into small increments called iterations or sprints. Each iteration results in a working product that can be reviewed and tested.
- Customer Collaboration: Customers are involved throughout the development process, providing feedback and guidance to ensure the final product meets their requirements.
- Adaptability: Agile teams are flexible and able to respond to changes in requirements or priorities quickly, ensuring that the project stays on track.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular retrospectives allow teams to reflect on their processes and make adjustments for better efficiency and quality.
The Agile SDLC Phases:
Planning:
In this phase, the project scope is defined, requirements are gathered, and the team creates a roadmap for the project.
Analysis:
The team analyzes the requirements in detail, breaking them down into user stories or tasks that can be prioritized for development.
Design:
In this phase, the team designs the architecture of the software based on the requirements identified earlier. Design decisions are made collaboratively with input from all team members.
Development:
The actual coding of the software takes place in this phase. Developers work in short iterations to build features incrementally.
Testing:
Each iteration undergoes rigorous testing to ensure that all features work as expected and meet quality standards.
Deployment:
The completed features are integrated into a working product and deployed for user feedback. Continuous integration and deployment practices help streamline this phase.
Review & Retrospective:
The team reviews the completed work with stakeholders for feedback and conducts a retrospective to identify areas for improvement in future iterations.
In conclusion, Agile SDLC offers a dynamic and collaborative approach to software development that prioritizes customer satisfaction, adaptability, and continuous improvement. By embracing agility in their processes, teams can deliver high-quality software efficiently while responding effectively to changing requirements and market demands.
Exploring Agile SDLC: Key Principles, Benefits, and Best Practices
- What is Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
- What are the key principles of Agile SDLC?
- How does Agile SDLC differ from traditional waterfall model?
- What are the benefits of using Agile SDLC in software development?
- What roles are involved in an Agile SDLC team?
- How do you handle changes in requirements during an Agile SDLC project?
- What tools are commonly used in Agile SDLC projects?
- How do you measure the success of an Agile SDLC project?
- Can non-software development teams benefit from adopting Agile principles?
What is Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
The Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a methodology that revolutionizes traditional software development practices by emphasizing flexibility, collaboration, and iterative progress. Unlike the linear waterfall model, Agile SDLC breaks down the development process into smaller, manageable iterations known as sprints. These sprints allow for continuous feedback, adaptation to changing requirements, and early delivery of working software components. By prioritizing customer collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement, Agile SDLC ensures that software projects are delivered efficiently and effectively while meeting evolving business needs.
What are the key principles of Agile SDLC?
The key principles of Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) revolve around iterative development, customer collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement. Agile SDLC breaks down projects into manageable iterations or sprints, allowing for the delivery of working software increments that can be reviewed and tested regularly. Customer collaboration is emphasized throughout the process to ensure that the final product meets their requirements. The adaptability of Agile teams enables them to respond quickly to changes in priorities or requirements, maintaining project momentum. Continuous improvement is achieved through regular retrospectives, where teams reflect on their processes and make adjustments for enhanced efficiency and quality in subsequent iterations.
How does Agile SDLC differ from traditional waterfall model?
In comparing Agile SDLC with the traditional waterfall model, one of the key distinctions lies in their approach to project management and software development. The waterfall model follows a sequential, linear process where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next, with minimal flexibility for changes once a phase is finished. On the other hand, Agile SDLC emphasizes iterative and collaborative development, breaking the project into smaller increments or sprints that are developed and tested incrementally. This allows for greater adaptability to changing requirements, continuous feedback from stakeholders, and early delivery of working software components. Agile SDLC promotes customer collaboration and embraces change as a natural part of the development process, offering a more flexible and responsive approach compared to the rigid structure of the waterfall model.
What are the benefits of using Agile SDLC in software development?
Utilizing Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in software development offers a multitude of benefits. One key advantage is increased flexibility, as Agile allows for iterative development, enabling teams to adapt to changing requirements and market conditions quickly. Another benefit is enhanced collaboration, as Agile promotes regular communication and feedback among team members and stakeholders, leading to improved transparency and alignment. Additionally, Agile SDLC fosters faster delivery of high-quality software through its incremental approach, reducing time-to-market and enhancing customer satisfaction. Overall, the adoption of Agile methodologies can result in more efficient processes, higher productivity levels, and ultimately better outcomes for software development projects.
What roles are involved in an Agile SDLC team?
In an Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) team, various roles collaborate to ensure the success of the project. Some key roles typically found in an Agile SDLC team include the Product Owner, who represents the customer and defines project requirements; the Scrum Master, responsible for facilitating team collaboration and removing obstacles; and the Development Team, comprising cross-functional members who work together to deliver increments of working software. Additionally, stakeholders such as users, testers, and business analysts may also play essential roles in providing feedback and guidance throughout the development process. This collaborative approach ensures that all perspectives are considered, leading to a successful outcome in Agile projects.
How do you handle changes in requirements during an Agile SDLC project?
In Agile SDLC projects, handling changes in requirements is a common challenge that teams face. One effective approach to managing changing requirements is through open communication and collaboration. By maintaining close contact with stakeholders and involving them in regular feedback sessions, teams can quickly identify and address evolving needs. Additionally, Agile methodologies emphasize flexibility and adaptability, allowing for adjustments to be made easily within short development cycles. Prioritizing requirements based on business value and impact also helps in accommodating changes while ensuring that the project stays on track. Ultimately, by embracing change as a natural part of the process and leveraging the iterative nature of Agile SDLC, teams can effectively manage shifting requirements to deliver a successful and responsive product.
What tools are commonly used in Agile SDLC projects?
In Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) projects, various tools are commonly used to enhance collaboration, communication, and project management efficiency. Some popular tools include Jira, Trello, and Asana for task tracking and project planning. Version control systems like Git help teams manage code changes effectively. Continuous integration tools such as Jenkins automate the build and testing processes. Communication tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams facilitate real-time collaboration among team members. Agile teams often use tools like Burndown charts or Kanban boards to visualize progress and identify bottlenecks in the development process. These tools play a crucial role in supporting Agile principles and practices throughout the project lifecycle.
How do you measure the success of an Agile SDLC project?
Measuring the success of an Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) project involves assessing various key performance indicators that reflect the project’s efficiency, quality, and alignment with stakeholder expectations. Common metrics used to evaluate Agile SDLC projects include on-time delivery of features, customer satisfaction levels, team velocity, defect density, and adherence to project budget. Additionally, the ability to adapt to changing requirements, continuous improvement in product quality through feedback loops, and overall team morale are also crucial indicators of success in an Agile SDLC project. By tracking these metrics throughout the project lifecycle and incorporating feedback from stakeholders, teams can gauge their progress and make informed decisions to ensure successful project outcomes.
Can non-software development teams benefit from adopting Agile principles?
Many non-software development teams can indeed benefit from adopting Agile principles. While Agile was originally designed for software development, its core values of collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement can be applied to various industries and team settings. By embracing Agile principles, non-software development teams can enhance their project management processes, increase transparency and communication, respond more effectively to changes or challenges, and deliver value to their stakeholders in a more efficient and iterative manner. The flexibility and customer-centric approach of Agile can help non-software development teams improve productivity, quality, and overall project outcomes.