Understanding What SDLC Is: A Comprehensive Guide to Software Development Life Cycle
Understanding Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
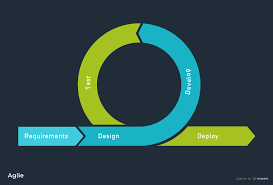
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured process that guides the development of software applications from inception to deployment and maintenance. It is a systematic approach to software development that ensures high-quality, well-organized, and cost-effective solutions.
The Phases of SDLC
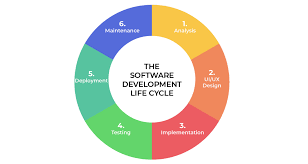
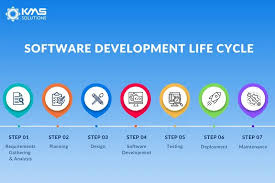
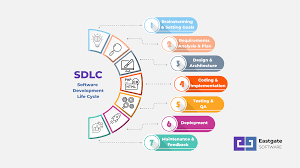
SDLC typically consists of several phases, each with its own set of activities and deliverables:
- Planning: In this phase, project requirements are gathered, feasibility studies are conducted, and a project plan is created.
- Analysis: The system requirements are analyzed in detail to understand the scope of the project and define the functionalities needed.
- Design: This phase involves creating a detailed design of the system architecture, database structure, user interface, and other components.
- Implementation: The actual coding of the software takes place in this phase based on the design specifications.
- Testing: The software is thoroughly tested to identify and fix any defects or issues before deployment.
- Deployment: The software is deployed to the production environment after successful testing.
- Maintenance: Post-deployment, ongoing maintenance and support activities ensure that the software continues to function effectively.
The Importance of SDLC
An effective SDLC process offers numerous benefits, including:
- Better control over project timelines and costs
- Improved communication among stakeholders
- Higher quality software products with fewer defects
- Easier maintenance and scalability of applications
In Conclusion
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is an essential framework for developing reliable software solutions. By following a structured approach through its various phases, organizations can ensure successful outcomes for their projects while meeting user requirements and business objectives.
Understanding the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC): Key Phases, Importance, and Common Challenges
- What is SDLC and why is it important?
- What are the different phases of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
- How does SDLC help in ensuring the quality of software products?
- What role does testing play in the SDLC process?
- How can organizations benefit from following a structured SDLC approach?
- What are some common challenges faced during the implementation of SDLC?
What is SDLC and why is it important?
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a systematic process that guides the development of software applications from inception to deployment and maintenance. It is crucial because it provides a structured framework for managing and executing software projects efficiently. SDLC helps ensure that software products are developed with high quality, meet user requirements, adhere to budget and timeline constraints, and are maintainable in the long run. By following the phases of SDLC, organizations can minimize risks, improve communication among project stakeholders, and deliver successful software solutions that align with business goals.
What are the different phases of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) comprises several distinct phases that guide the development process of a software application from inception to deployment and maintenance. These phases typically include planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Each phase has its own set of activities and objectives aimed at ensuring the successful and systematic progression of the software development project. By following these well-defined phases within the SDLC framework, organizations can effectively manage their software development projects and deliver high-quality solutions that meet user requirements and business goals.
How does SDLC help in ensuring the quality of software products?
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of software products by providing a structured framework that guides the development process from start to finish. By following the defined phases of SDLC, including planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance, developers can systematically identify and address potential issues at each stage. This approach allows for thorough testing and validation of the software before deployment, leading to higher-quality products with fewer defects. Additionally, SDLC promotes collaboration among stakeholders, clear documentation of requirements and design specifications, and effective project management practices—all of which contribute to delivering software solutions that meet user expectations and business needs.
What role does testing play in the SDLC process?
Testing plays a crucial role in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process. It is a fundamental phase that ensures the quality and reliability of the software being developed. Testing helps identify and rectify defects, bugs, and issues in the software before it is deployed to production. By conducting thorough testing at different stages of the SDLC, developers can validate that the software meets all requirements, functions as intended, and delivers a seamless user experience. Effective testing not only enhances the overall quality of the product but also reduces risks associated with post-deployment failures, ultimately contributing to successful project outcomes.
How can organizations benefit from following a structured SDLC approach?
Organizations can benefit significantly from following a structured Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) approach. By adhering to a well-defined SDLC process, organizations can ensure better control over project timelines and costs, leading to more predictable outcomes. A structured SDLC approach also promotes improved communication among project stakeholders, fostering collaboration and alignment towards common goals. Moreover, following an SDLC framework results in higher quality software products with fewer defects, enhancing overall customer satisfaction and reducing the need for costly rework. Additionally, the systematic nature of SDLC facilitates easier maintenance and scalability of applications, enabling organizations to adapt to changing business requirements more efficiently.
What are some common challenges faced during the implementation of SDLC?
During the implementation of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), several common challenges may arise. One significant challenge is managing changing requirements, as stakeholders may introduce new needs or modifications during the development process, leading to scope creep. Another challenge is maintaining clear communication among team members and stakeholders to ensure alignment on project goals and expectations. Additionally, resource constraints, such as budget limitations or staffing issues, can impact the timely delivery of the project. Addressing these challenges requires proactive planning, effective collaboration, and adaptability throughout the SDLC stages to mitigate risks and ensure successful project outcomes.