Mastering SDLC Methodologies with Guru99’s Expert Guidance
The Ultimate Guide to Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) by Guru99
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a crucial process in software development that outlines the steps involved in creating, testing, and deploying software applications. Guru99 is a leading platform that offers comprehensive resources and guides on SDLC to help developers and organizations understand and implement this process effectively.
What is SDLC?
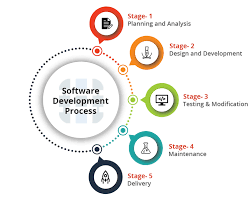
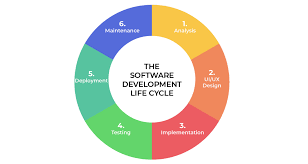
SDLC is a systematic approach to software development that ensures high-quality, reliable, and cost-effective software solutions. It consists of several phases, including planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Each phase has specific objectives and deliverables that contribute to the overall success of the project.
Guru99’s Expertise in SDLC
Guru99 provides in-depth tutorials, articles, and videos on SDLC that cover various methodologies such as Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, and DevOps. Their expert guidance helps developers gain a comprehensive understanding of each phase of the SDLC process and how to apply best practices for successful software development projects.
Benefits of Following SDLC
By following SDLC principles advocated by Guru99, developers can benefit from:
- Improved project management
- Enhanced collaboration among team members
- Better risk management
- Higher quality software products
- Increased customer satisfaction
Conclusion
Guru99’s expertise in SDLC makes it a valuable resource for developers looking to enhance their software development skills and deliver successful projects. By following the guidance provided by Guru99 on SDLC methodologies and best practices, developers can streamline their development processes and achieve better outcomes for their software projects.
Master Software Development with Expert Insights and Best Practices from SDLC Guru99
- Comprehensive tutorials on various SDLC methodologies
- Expert guidance for each phase of the software development process
- In-depth articles and videos for easy learning
- Clear explanation of best practices in software development
- Helps improve project management skills
- Enhances collaboration among team members
- Provides insights into risk management strategies
- Ensures higher quality software products
- Increases customer satisfaction through successful project delivery
Challenges of Using Guru99 for SDLC Learning: Depth, Updates, and User Experience
- Some tutorials may lack depth and advanced topics
- Limited interactive learning tools on the platform
- Not all content may be regularly updated to reflect the latest industry trends
- May require additional external resources for a more comprehensive understanding of certain SDLC concepts
- Navigation on the website could be improved for better user experience
- The platform may not cater to all levels of expertise, from beginners to advanced developers
Comprehensive tutorials on various SDLC methodologies
Guru99 stands out for its comprehensive tutorials on various Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) methodologies. Whether it’s Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, or DevOps, Guru99 provides detailed and insightful guidance to help developers understand and implement different SDLC approaches effectively. By offering in-depth tutorials on a wide range of methodologies, Guru99 empowers developers to choose the right approach for their projects and enhance their software development skills.
Expert guidance for each phase of the software development process
Guru99 offers expert guidance for each phase of the software development process, ensuring that developers have the necessary support and knowledge to navigate through planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance seamlessly. By providing detailed insights and best practices for each stage of the SDLC, Guru99 empowers developers to make informed decisions and execute tasks effectively, ultimately leading to the successful delivery of high-quality software solutions.
In-depth articles and videos for easy learning
Guru99’s SDLC resources stand out for their in-depth articles and videos, offering a comprehensive learning experience that caters to both beginners and experienced professionals in the software development field. With clear explanations and practical examples, these resources make complex SDLC concepts easy to grasp, empowering learners to enhance their skills and knowledge effectively.
Clear explanation of best practices in software development
Guru99’s SDLC resources excel in providing a clear explanation of best practices in software development. By offering detailed insights into industry-proven methodologies and techniques, Guru99 equips developers with the knowledge and understanding needed to implement effective strategies throughout the software development life cycle. This clarity empowers professionals to make informed decisions, improve project outcomes, and deliver high-quality software solutions that meet the highest standards of excellence.
Helps improve project management skills
Guru99’s comprehensive resources on Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) play a crucial role in helping individuals enhance their project management skills. By following Guru99’s guidance on SDLC methodologies, aspiring project managers can learn how to effectively plan, execute, and monitor software development projects. The detailed insights provided by Guru99 empower individuals to streamline project workflows, allocate resources efficiently, and ensure timely delivery of high-quality software solutions. Overall, utilizing Guru99’s expertise in SDLC can significantly contribute to the improvement of project management skills and the successful execution of software development initiatives.
Enhances collaboration among team members
One significant advantage of utilizing SDLC methodologies from Guru99 is that it enhances collaboration among team members. By following a structured approach to software development, team members are encouraged to work together closely at each phase of the project. This collaborative environment fosters communication, idea sharing, and problem-solving, leading to improved teamwork and ultimately better outcomes for the software development project.
Provides insights into risk management strategies
Guru99’s SDLC resources offer valuable insights into risk management strategies, helping developers and organizations effectively identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks throughout the software development life cycle. By understanding and implementing these strategies, users can proactively address challenges, minimize project disruptions, and enhance the overall success of their software projects. Guru99’s focus on risk management empowers individuals to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to ensure the delivery of high-quality software solutions.
Ensures higher quality software products
By emphasizing the importance of following Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) methodologies, Guru99 ensures that developers can deliver higher quality software products. By adhering to structured processes and best practices throughout the SDLC phases, developers can effectively identify and address issues early on, leading to more reliable and robust software solutions. Guru99’s guidance on SDLC helps developers prioritize quality assurance measures, testing procedures, and continuous improvement efforts, ultimately resulting in software products that meet or exceed user expectations.
Increases customer satisfaction through successful project delivery
By emphasizing successful project delivery as a key benefit, SDLC Guru99 ultimately increases customer satisfaction. By following the structured approach and best practices advocated by Guru99, developers can ensure that software projects are completed on time, within budget, and meet or exceed customer expectations. This commitment to delivering high-quality software solutions leads to satisfied customers who trust in the expertise and reliability of the development team.
Some tutorials may lack depth and advanced topics
While Guru99 offers valuable resources on Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), it is important to note that some tutorials provided by the platform may lack depth and coverage of advanced topics. This limitation could potentially hinder developers seeking in-depth knowledge and expertise in certain areas of SDLC. It is advisable for users to supplement their learning with additional resources or seek advanced tutorials elsewhere to ensure a comprehensive understanding of all aspects of the software development process.
Limited interactive learning tools on the platform
One notable drawback of SDLC Guru99 is the limited availability of interactive learning tools on the platform. While Guru99 offers comprehensive resources and guides on software development life cycle methodologies, the lack of interactive tools may hinder users’ engagement and hands-on learning experience. Interactive tools such as simulations, coding exercises, or interactive quizzes can enhance the learning process by providing practical application opportunities and reinforcing key concepts effectively. Incorporating more interactive learning tools could further enrich the educational experience on SDLC Guru99 and cater to a wider range of learning preferences among users.
Not all content may be regularly updated to reflect the latest industry trends
One drawback of using SDLC resources from Guru99 is that not all content may be regularly updated to reflect the latest industry trends. This could potentially lead to users relying on outdated information, which may not align with current best practices or technological advancements in the software development field. Staying informed about the latest trends and updates is crucial in a rapidly evolving industry like software development, and users should exercise caution when utilizing resources that may not be consistently updated to ensure they are working with the most relevant and up-to-date information available.
May require additional external resources for a more comprehensive understanding of certain SDLC concepts
One drawback of utilizing SDLC resources from Guru99 is that it may necessitate seeking additional external resources to gain a more thorough understanding of certain SDLC concepts. While Guru99 provides valuable tutorials and guides on software development life cycle methodologies, some users may find that supplementary materials are needed to delve deeper into specific aspects of the SDLC process. This limitation highlights the importance of exploring a variety of sources to ensure a comprehensive grasp of complex SDLC concepts.
Navigation on the website could be improved for better user experience
One drawback of using the SDLC resources on Guru99 is that the navigation on the website could be enhanced to provide a better user experience. Improving the website’s navigation would make it easier for users to locate specific SDLC tutorials, articles, and videos quickly, ultimately enhancing their overall learning experience. By addressing this issue, Guru99 could further optimize its platform and make it even more user-friendly for individuals seeking valuable insights into software development life cycle methodologies.
The platform may not cater to all levels of expertise, from beginners to advanced developers
While Guru99 offers valuable resources and guides on Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), one potential drawback is that the platform may not cater to all levels of expertise, from beginners to advanced developers. This limitation could pose a challenge for individuals seeking comprehensive support and guidance tailored to their specific skill levels within the SDLC process. It is important for users to assess their proficiency level in software development before relying solely on Guru99’s content to ensure they receive appropriate assistance and instruction throughout their learning journey.